
Energy Systems
An ecosystem consists of all the interactions between a group of organisms and their environment
-
It is comprised of both biotic components (i.e. communities) and abiotic components (i.e. habitat)
Ecosystems can vary in both size and complexity (a small pond and an ocean are both examples of ecosystems)
-
Ecosystems can also be described as closed or open depending on whether matter moves in and out of the system
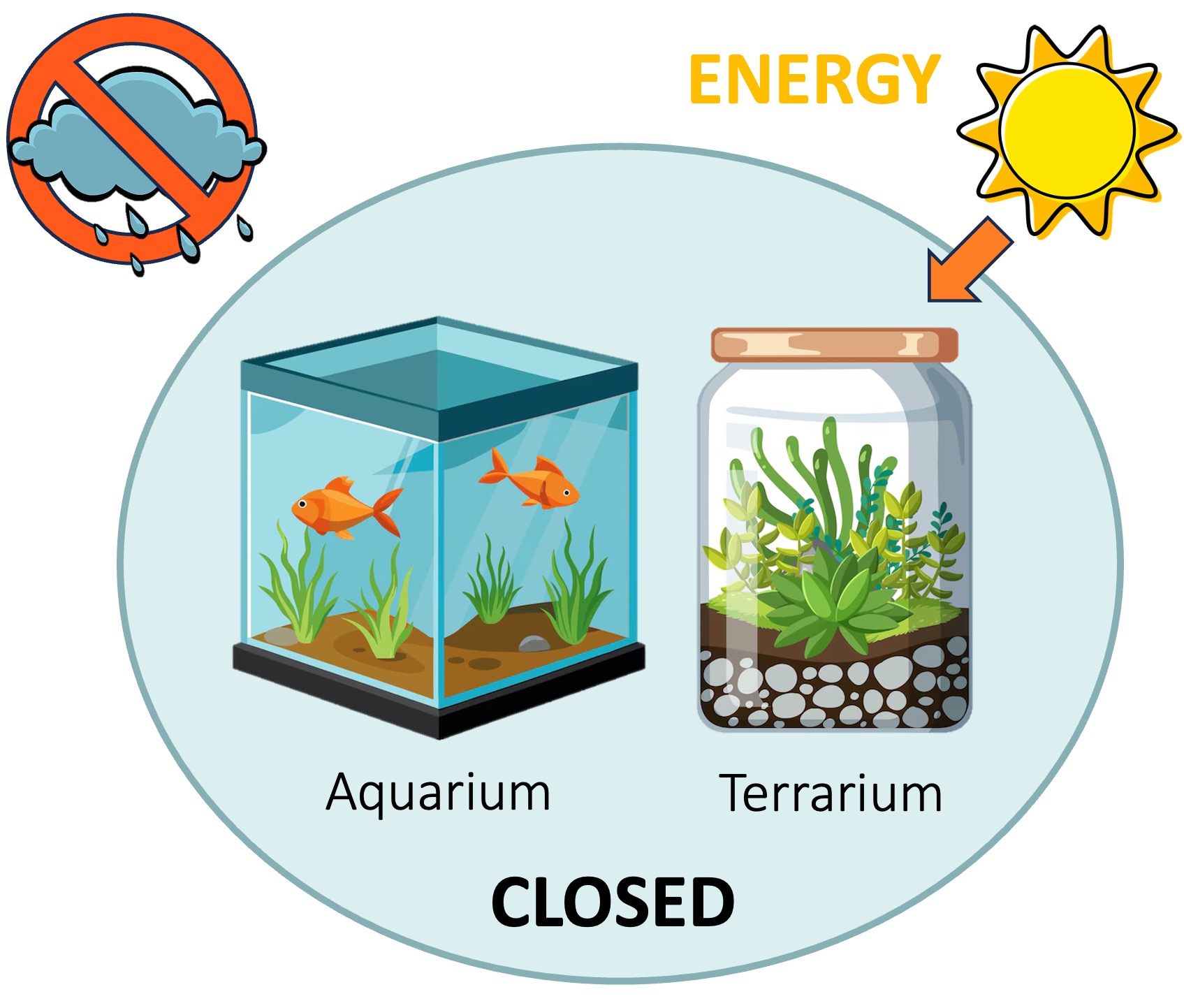
Closed Systems
A closed ecosystem exchanges energy but not matter with its surroundings – it is self-contained
-
While energy will flow through the system (enter and leave), matter remains and must be recycled
-
Mesocosms are examples of closed ecosystems – additionally, the entire Earth is considered a closed system (barring meteorites)
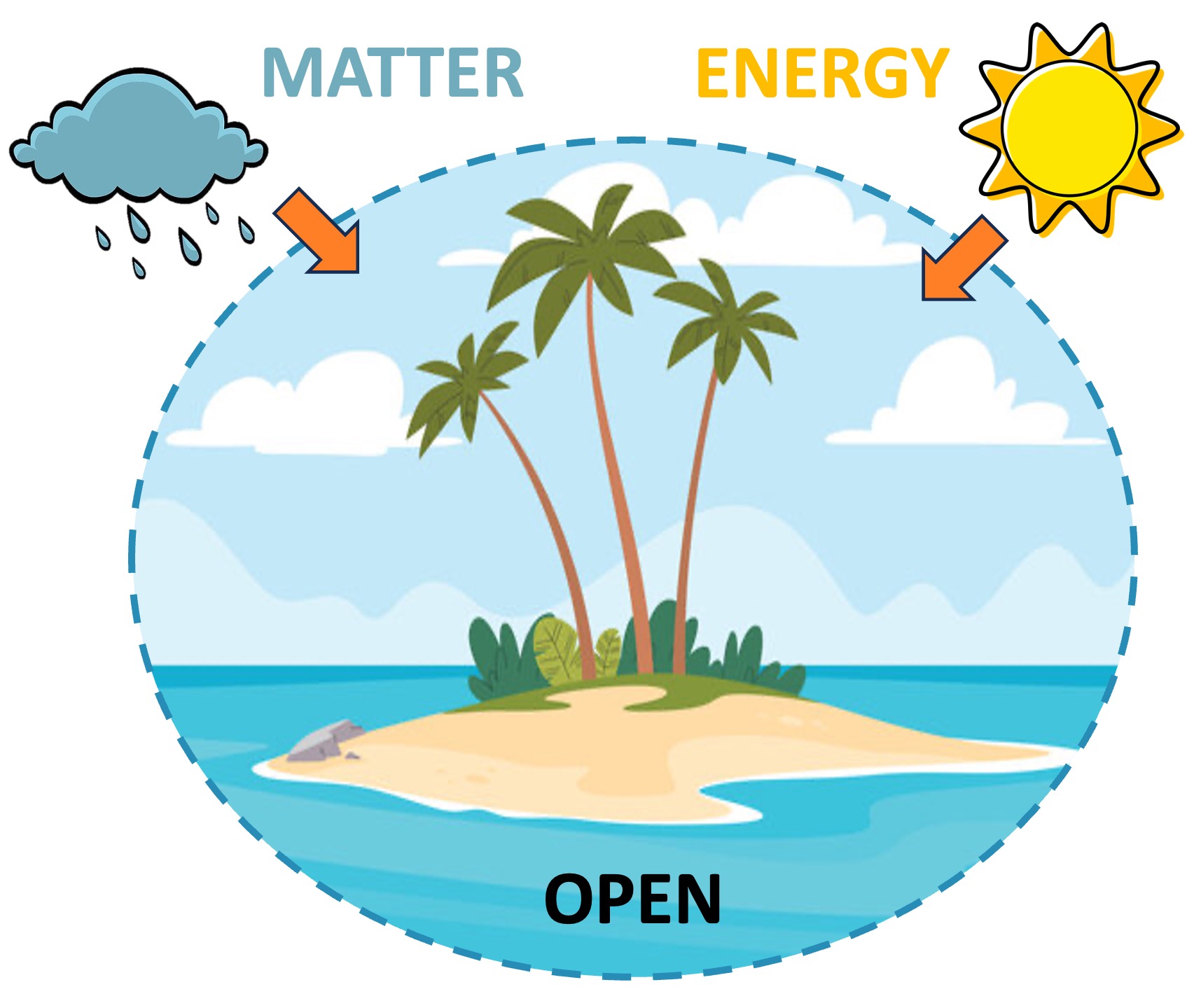
Open Systems
An open system exchanges both energy and matter with its surrounding environment
-
Energy is sourced from sunlight (photosynthesis) or produced via chemical reactions (chemosynthesis or cell respiration)
-
Matter can be transferred from outside the system (via animal migration, rainfall, dispersal by wind, etc.)
-
While most natural ecosystems are considered to be open, they are also considered to be largely self-contained (most organisms remain within a single ecosystem)
Closed vs Open Ecosystems






