Drug Interactions
Exogenous chemicals are substances that enter an organism from an external source and can interfere with the way neurons process signals from neurotransmitters
-
Examples of exogenous chemicals include medications, pollutants, pesticides, food additives, narcotics and toxins in venoms
Neonicotinoids
-
Neonicotinoids are pesticides that are structurally similar to acetylcholine and can bind irreversibly to cholinergic receptors
-
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter released at neuromuscular junctions and triggers the contraction of muscles
-
Neurons produce an enzyme (acetylcholinesterase) that breaks down acetylcholine in the synapse to prevent overstimulation
-
Neonicotinoids bind to the acetylcholine receptor but cannot be broken down by acetylcholinesterase
-
This results in the continued depolarisation of post-synaptic neurons, leading to fatal convulsions and paralysis
-
Insects have a much higher proportion of cholinergic receptors than mammals, making neonicotinoids an effective pesticide
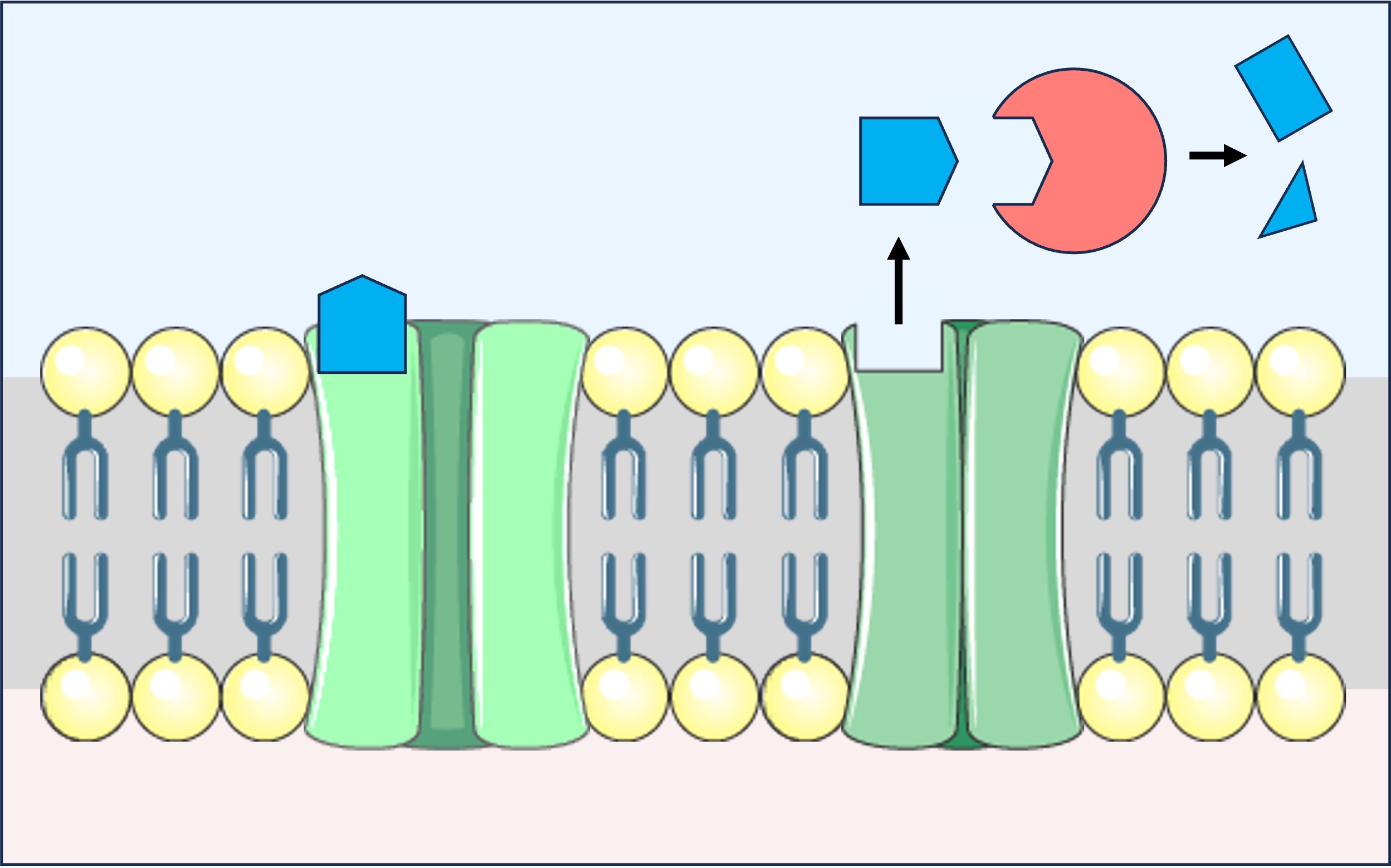
Acetylcholine Action
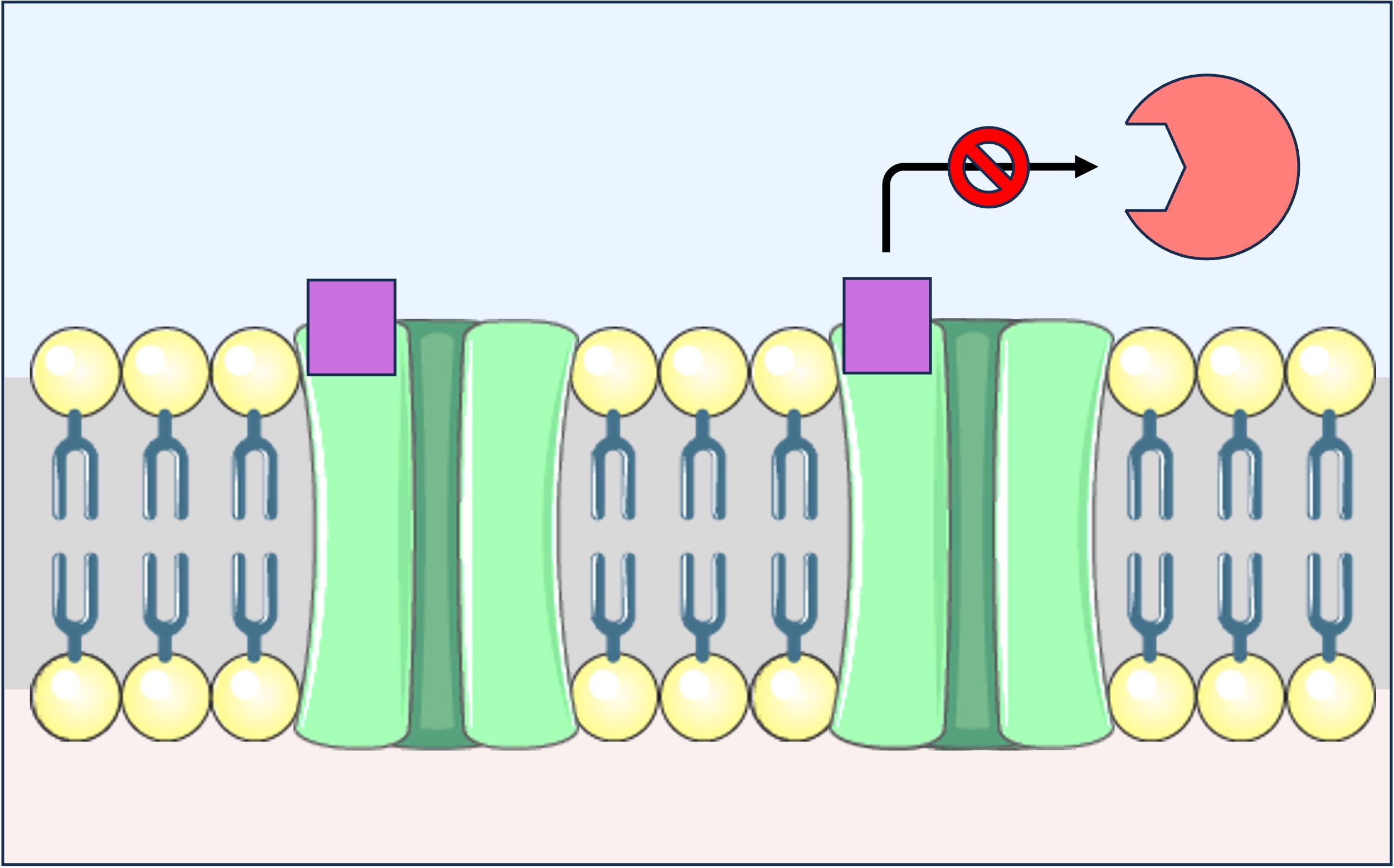
Neonicotinoid Action
Cocaine
-
Cocaine is a stimulant drug that acts on the mesolimbic pathway of the brain to trigger a sensation of euphoria
-
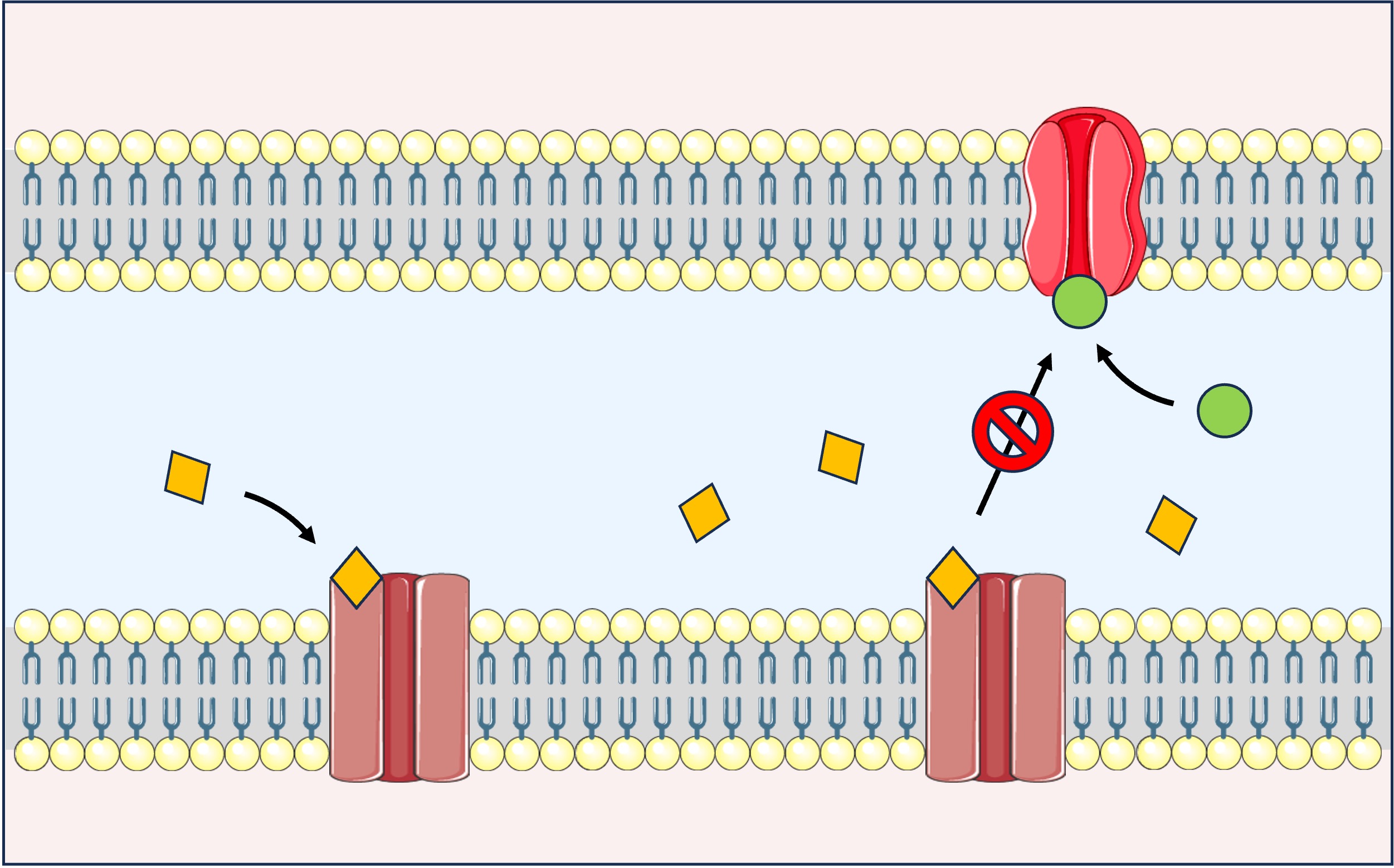
Cocaine binds to and blocks the dopamine reuptake pumps on pre-synaptic neurons in the dopamine reward pathway
-
This causes dopamine to accumulate within the synapse and continue to stimulate the mesolimbic system
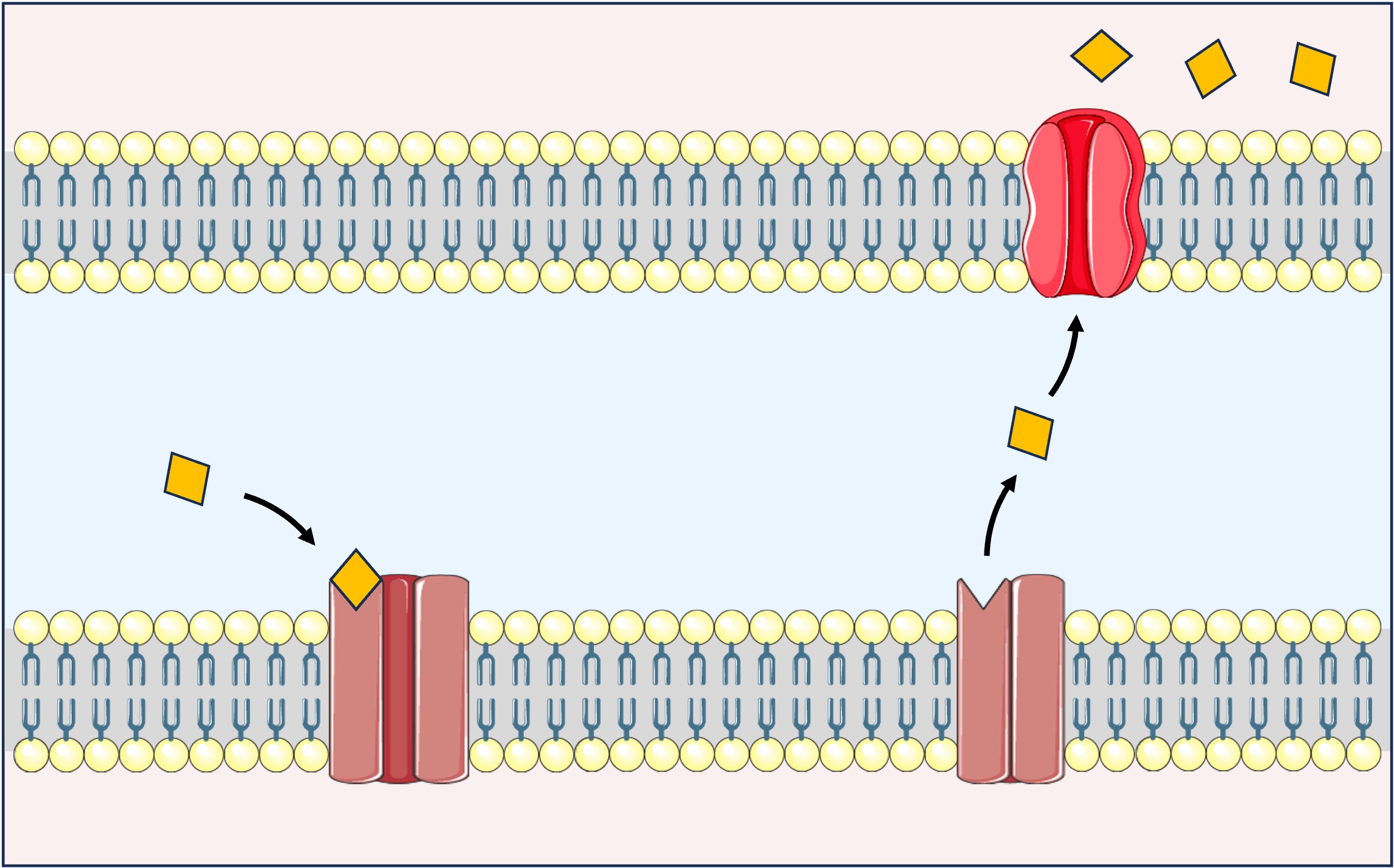
Dopamine Reuptake