Drawing Cells
Prokaryote: Bacteria
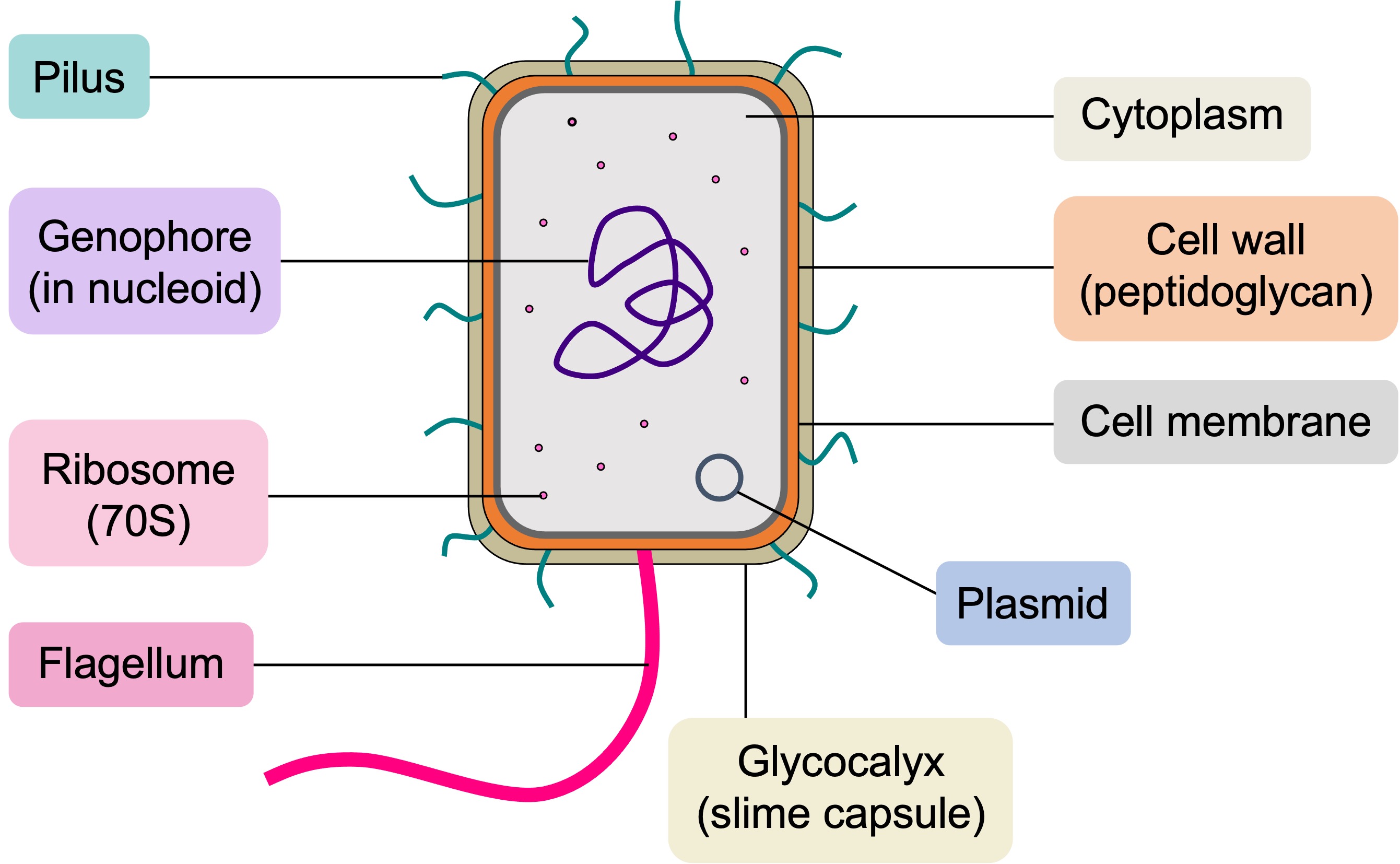
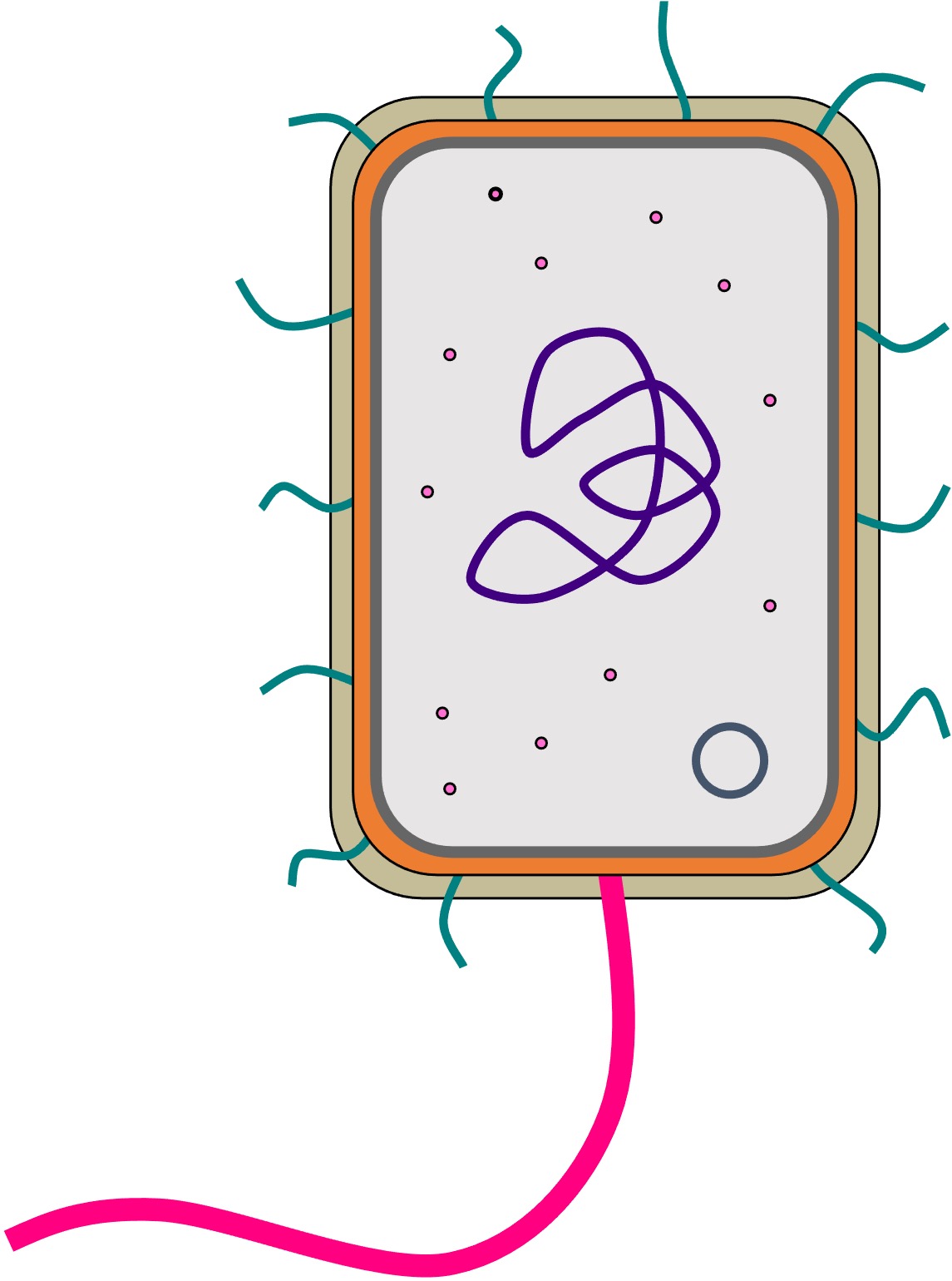
When drawing prokaryotic cells, the following should be included:
-
The genophore (bacterial chromosome) should be drawn as a loop (prokaryotic DNA is circular)
-
Pili and flagella should project from the cell wall (which is composed of peptidoglycan in bacteria)
-
Ribosomes should be drawn as filled in dots (not as empty circles) and labelled as 70S in size
-
A flagellum should be thicker than pili and significantly longer in length
-
The shape should be appropriate to the type of bacteria (hint: bacillus are rod-shaped)
Eukaryote: Animal Cell
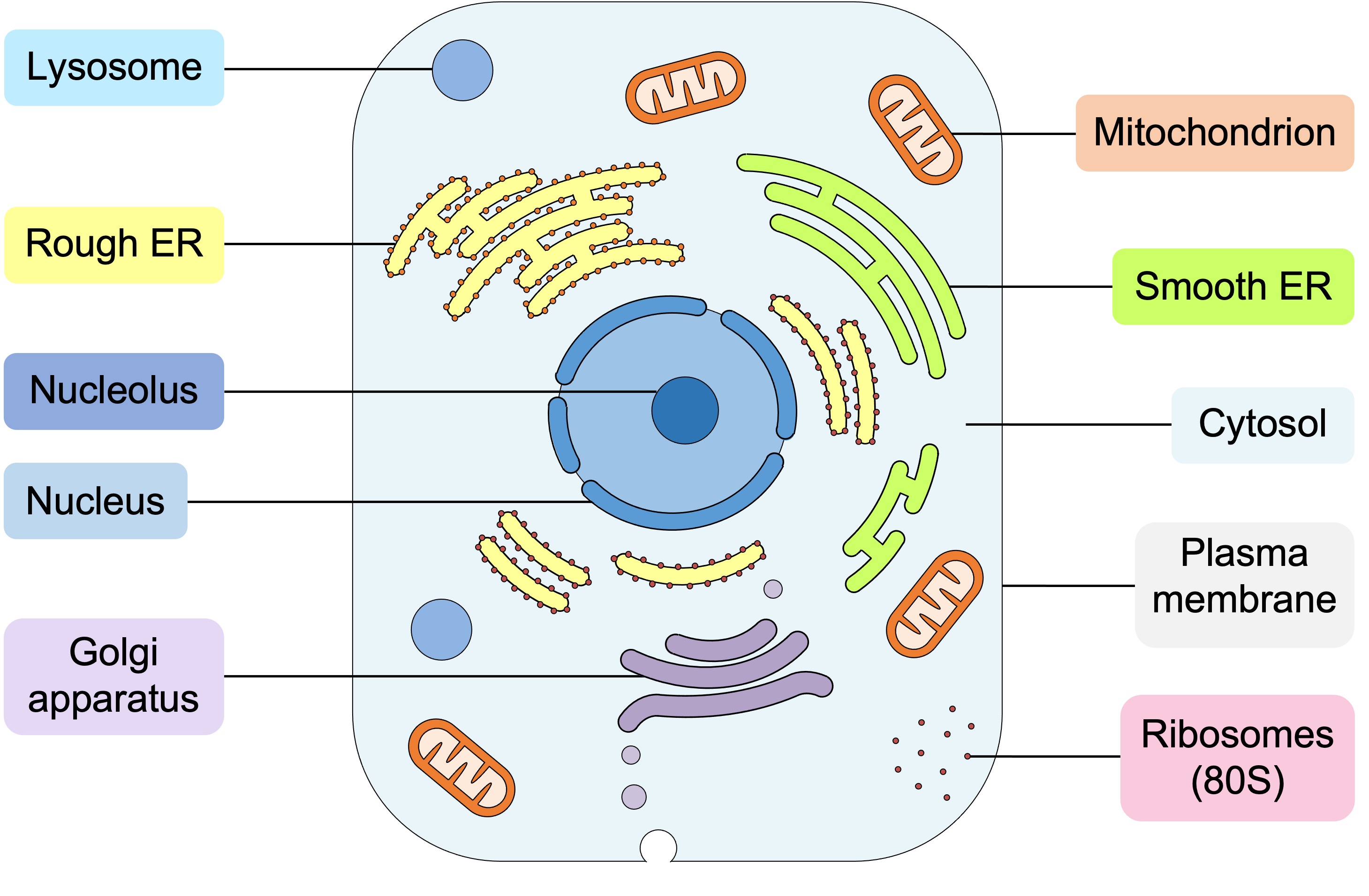

When drawing animal cells, the following should be included:
-
The nucleus should be a double membrane structure with pores (any chromosomes should be linear)
-
The ER network should be shown as connected membranes, but golgi membranes should be unconnected
-
Ribosomes should be drawn as filled in dots (not as empty circles) and labelled as 80S in size
-
Mitochondria should be sausage-shaped and the inner membrane highly folded (into cristae)
-
Peroxisomes, lysosomes and secretory vesicles should all look the same (except for the labelling)
Eukaryote: Plant Cell

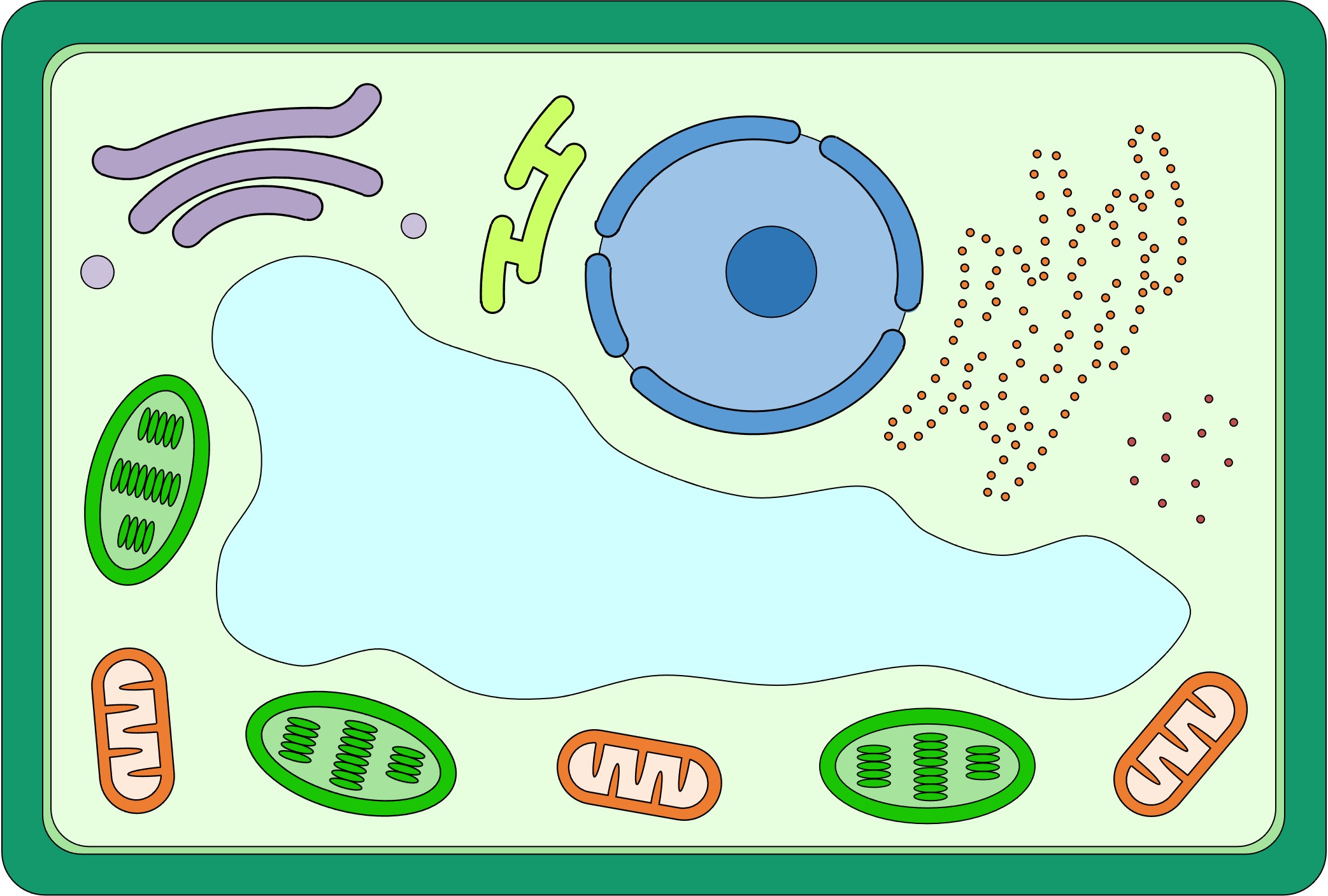
When drawing animal cells, the following should be included:
-
A large central vacuole should be included that occupies significant space within the cell
-
A cell wall made of cellulose should be included as a thicker line external to the plasma membrane
-
Chloroplasts should be double-membrane structures with internal stacks of flattened discs (grana)