DNA Tools
DNA can be manipulated using a number of molecular techniques in order to fulfil a wide array of biotechnological applications
-
DNA can be amplified via the polymerase chain reaction
-
DNA can be separated via agarose gel electrophoresis
PCR
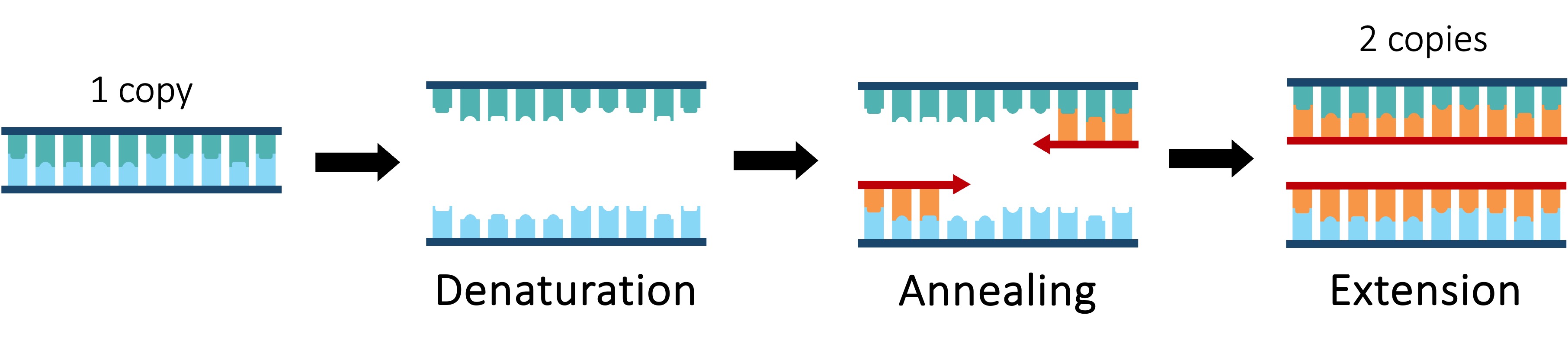
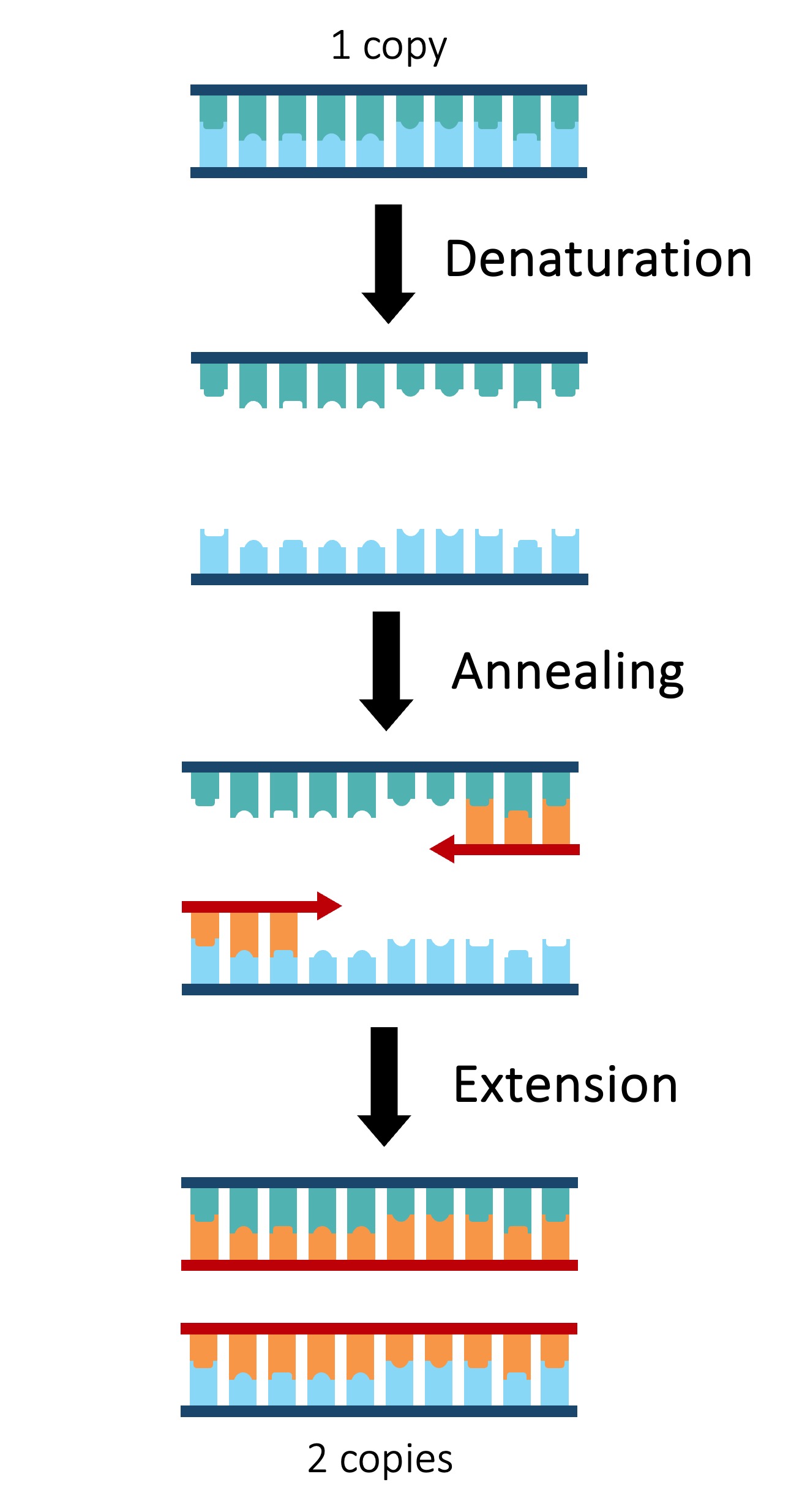
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an artificial method of replicating DNA under laboratory conditions
-
The PCR technique is used to amplify large quantities of a specific sequence of DNA from an initial minute sample
-
Each reaction doubles the amount of DNA – a standard PCR sequence of 30 cycles creates over 1 billion copies (230)
The reaction occurs in a thermal cycler and uses variations in temperature to control the replication process via three steps:
-
Denaturation – DNA sample is heated (~90ºC) to separate the two strands
-
Annealing – Sample is cooled (~55ºC) to allow primers to anneal (primers designate sequence to be copied)
-
Elongation – Sample is heated to the optimal temperature for a heat-tolerant polymerase (Taq) to function (~75ºC)
Taq polymerase is an enzyme isolated from the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus
-
As this enzyme’s optimal temperature is ~75ºC, it is able to function at the high temperatures used in PCR without denaturing
-
Taq polymerase extends the nucleotide chain from the primers – therefore primers are used to select the sequence to be copied
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a laboratory technique used to separate and isolate DNA fragments based on mass / size
-
DNA may be cut into fragments using restriction endonuclease – different DNA samples will generate different fragment lengths
-
Samples are placed in a block of gel and an electric current is applied which causes the samples to move through the gel
-
Fragments separate because DNA is negatively charged due to the presence of a phosphate group (PO43–) on each nucleotide
-
Smaller samples are less impeded by the gel matrix and hence will move faster through the gel
-
This causes samples of different sizes to separate as they travel at different speeds
Gel Electrophoresis Overview