DNA Structure
DNA is the nucleic acid that is used to pass hereditary information (genes) between generations of cells
-
It also contains the set of instructions that are used to produce proteins via RNA (it is the cell ‘blueprint')
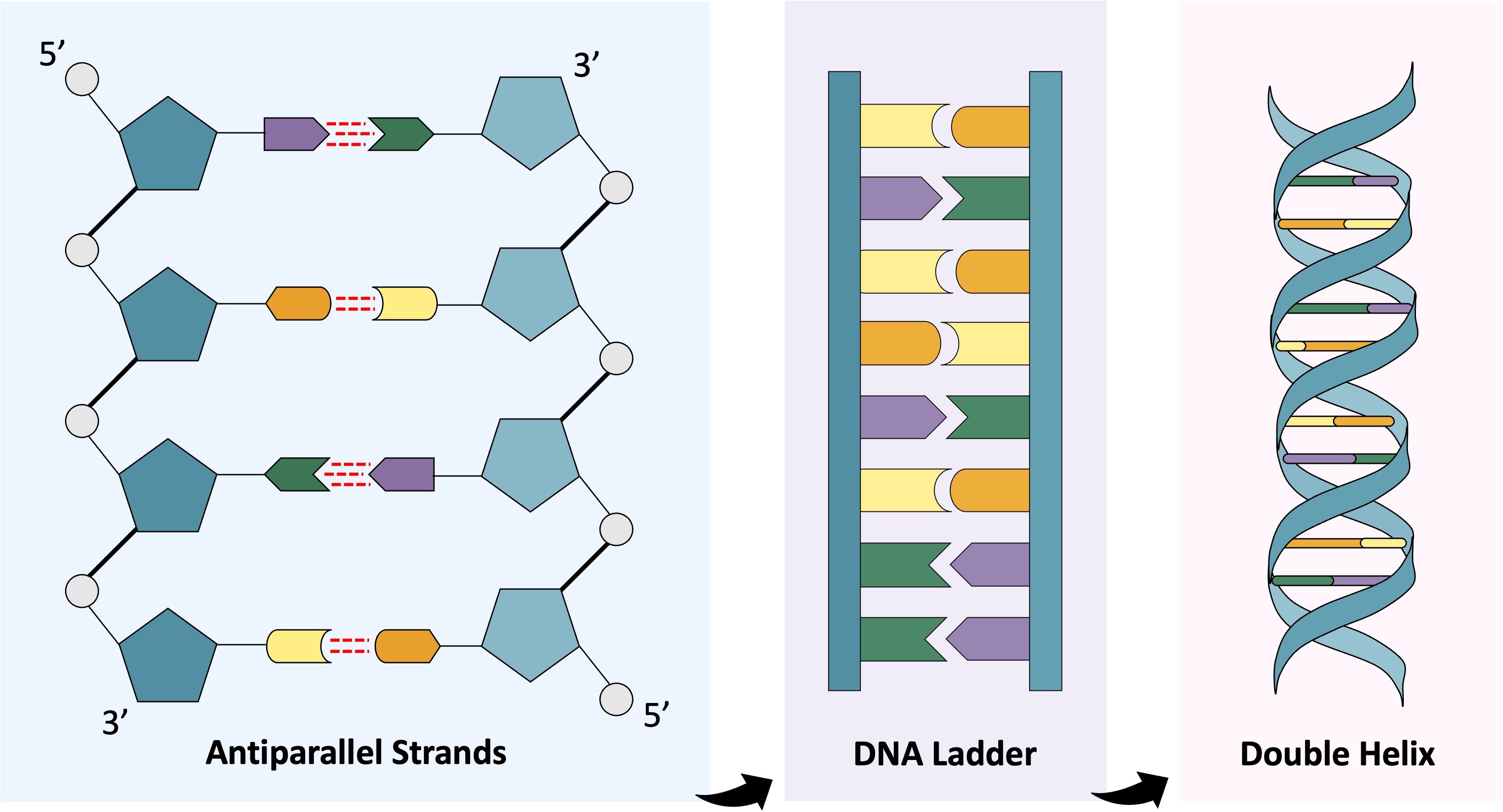
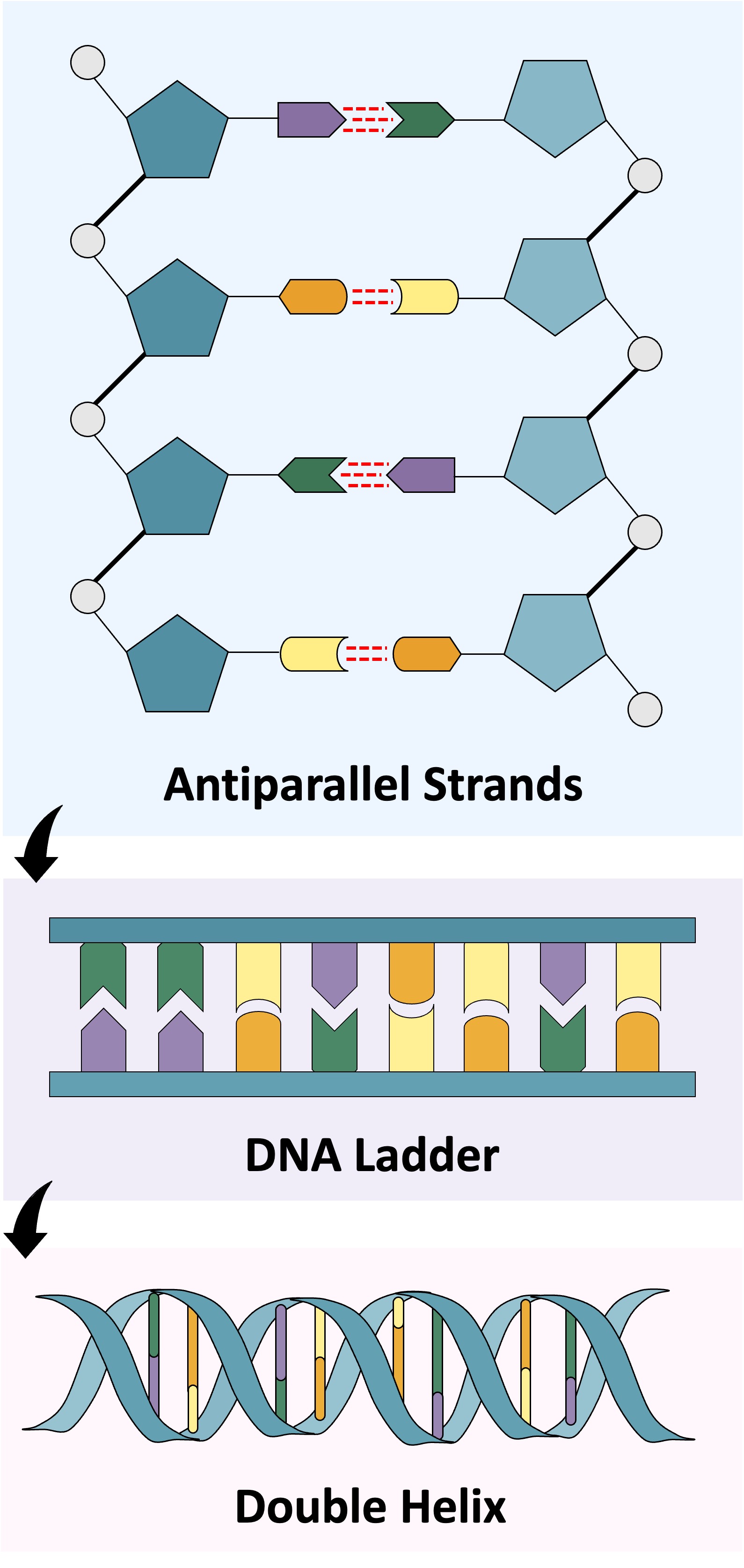
Unlike RNA, a DNA molecule is composed of two strands held together by hydrogen bonding between base pairs
-
Adenine pairs with thymine via two hydrogen bonds, while guanine and cytosine pair via three hydrogen bonds
In order to ensure the bases are facing each other and able to pair, the two strands must run in opposite directions (antiparallel)
-
The DNA molecule forms a ladder structure – the two backbones forming the struts and the base pairs acting as rungs
As the antiparallel chains lengthen, the strands will arrange themselves into the most stable energy configuration
-
This results in the double-stranded DNA forming a double helix (~10 – 15 bases per twist)
Being double standed helps to maintain the fidelity of the base sequence during replication, as one strand acts as a template for the other strand
DNA Structure