DNA Replication
DNA replication is a semi-conservative process whereby pre-existing strands act as templates for newly synthesised strands
-
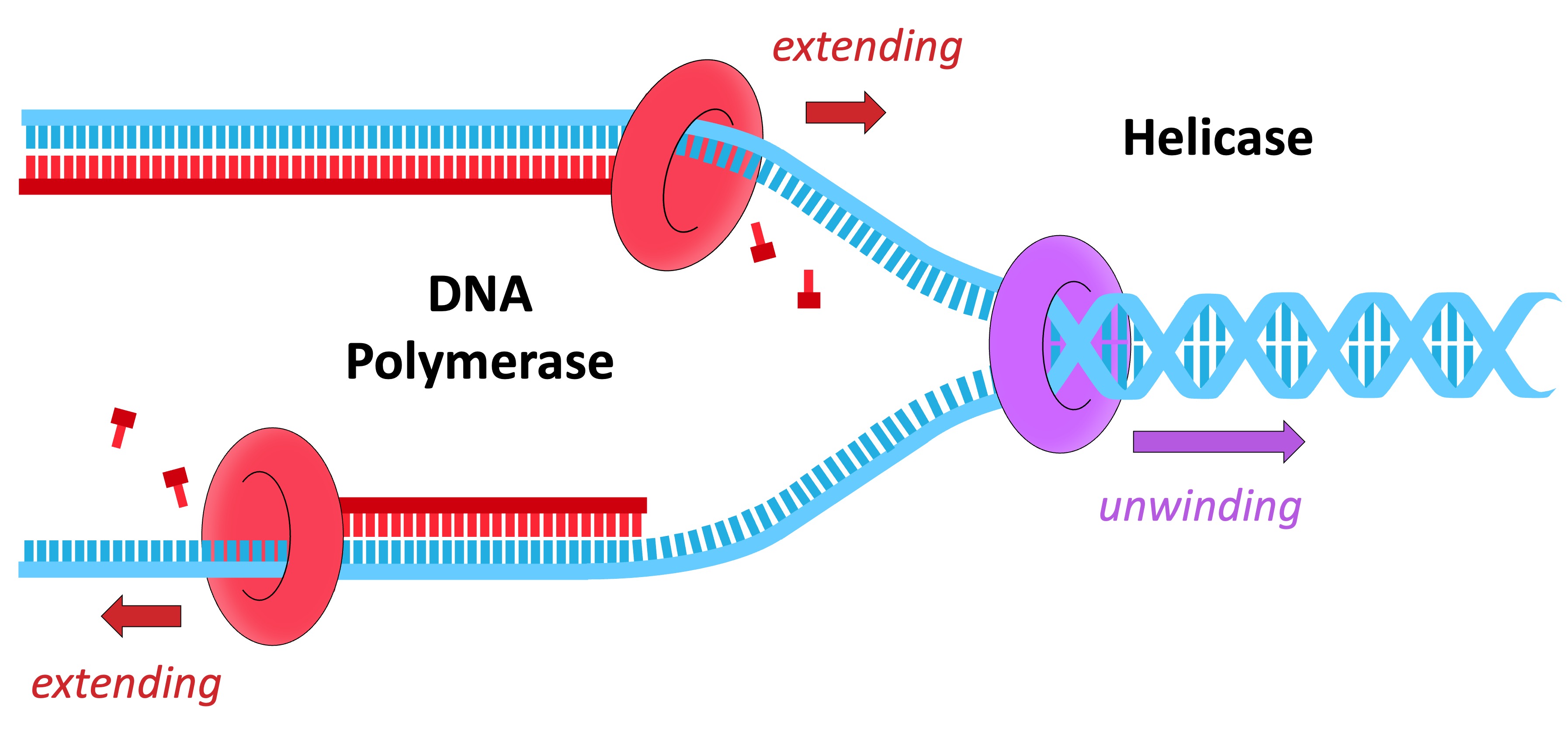
The process of DNA replication is coordinated by two key enzymes – helicase and DNA polymerase
Helicase
-
Helicase unwinds the double helix and separates the two polynucleotide strands
-
It does this by breaking the hydrogen bonds that exist between complementary base pairs
-
The two separated polynucleotide strands will act as templates for the synthesis of new complementary strands
DNA Polymerase
-
DNA polymerase synthesises new strands from the two parental template strands
-
Free deoxynucleoside triphosphates (nucleotides with 3 phosphate groups) align opposite their complementary base partner
-
DNA polymerase cleaves the two excess phosphates and uses the energy released to link the nucleotide to the new strand
DNA Replication Summary
DNA Replication Animation