

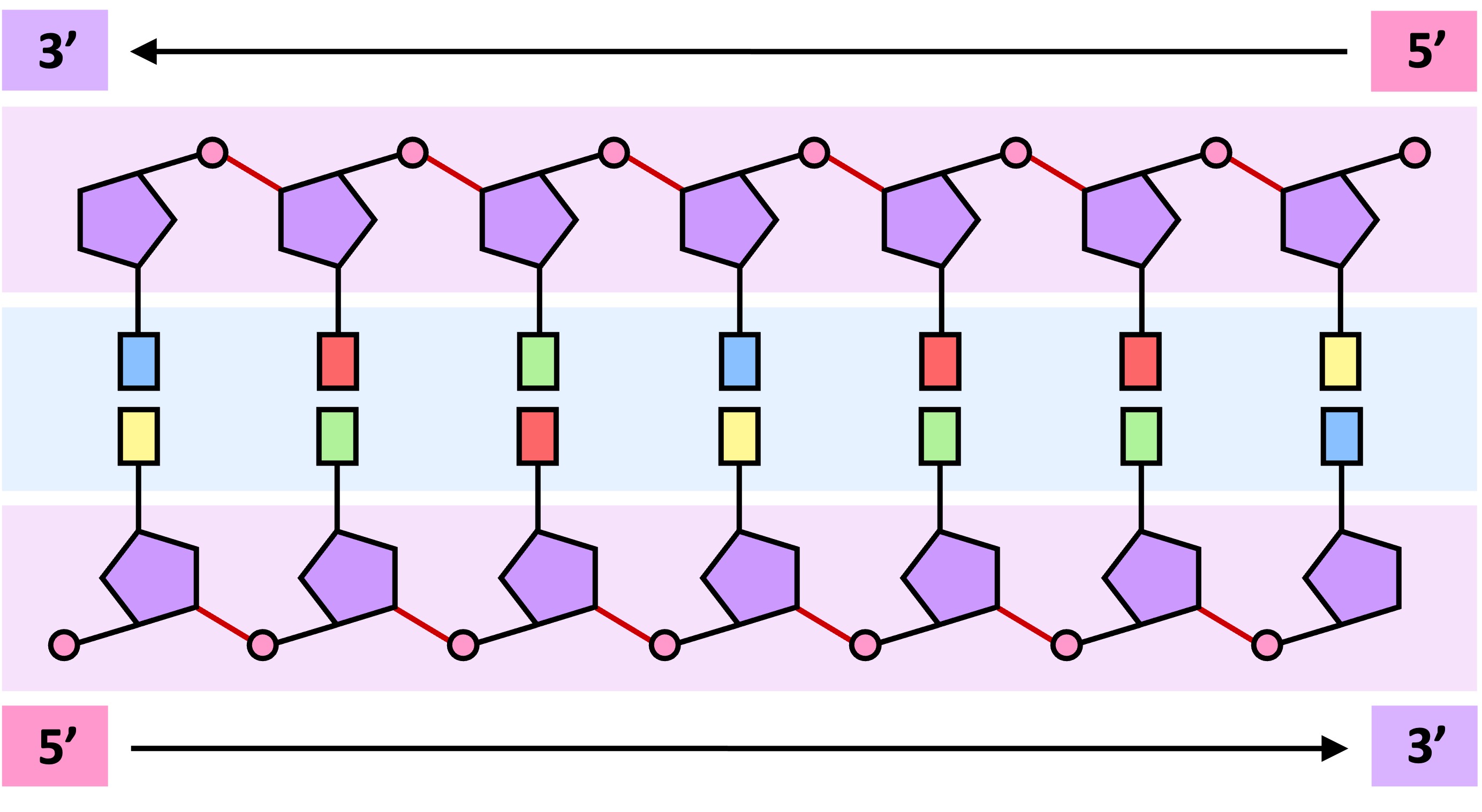
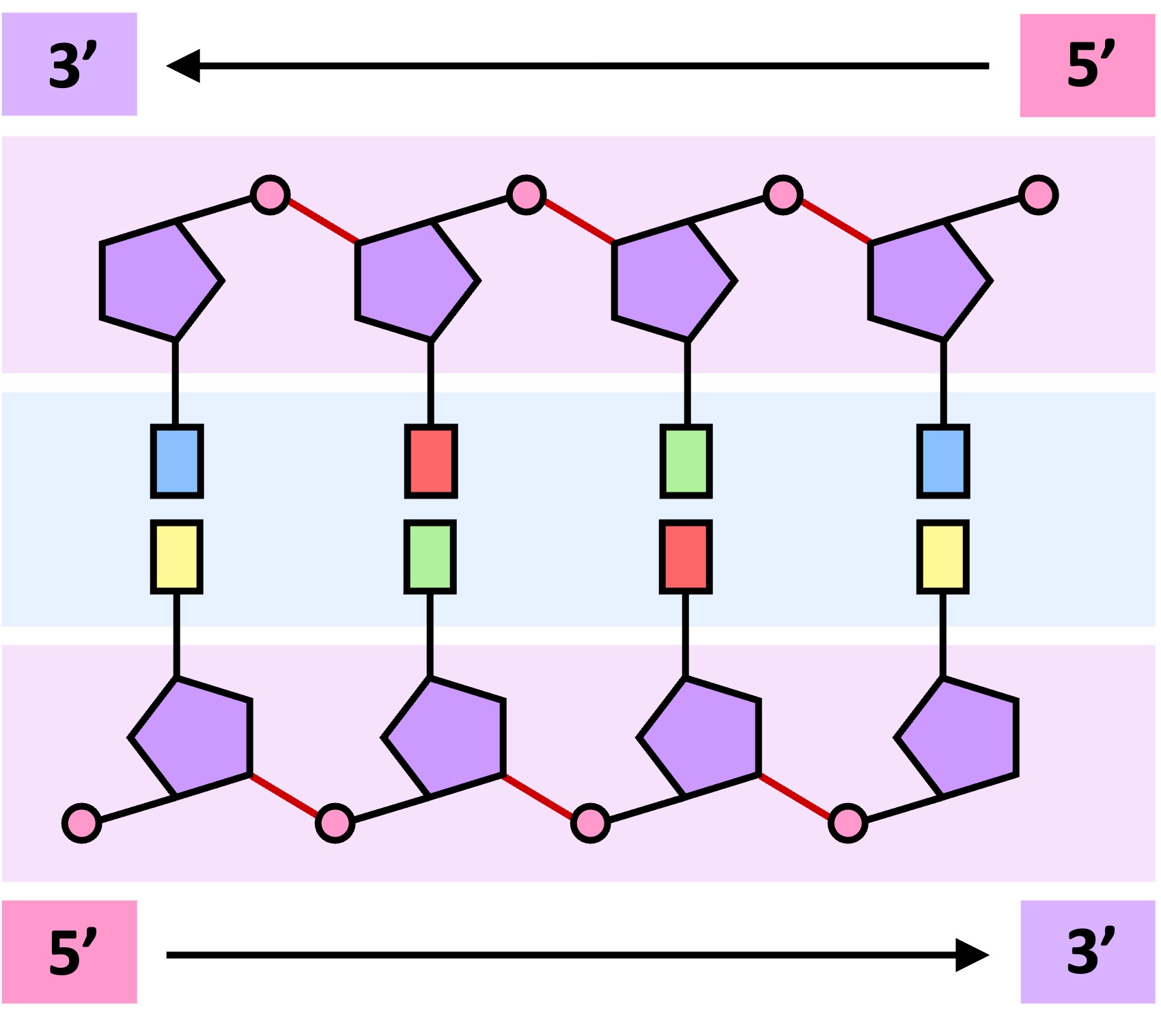
Directionality
Every nucleotide is made up of three basic components – a pentose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base
-
The carbon atoms in the pentose sugar are numbered, with the base attached to the 1’-carbon and the phosphate attached to the 5’-carbon
-
Nucleotides form long strands when the phosphate group of one nucleotide attaches to the sugar of another (at the 3’–hydroxyl position)
The 5' to 3' linkages in the sugar–phosphate backbone can be used to assign directionality to the DNA strand
-
As double stranded DNA is antiparallel, one strand runs from 5’ → 3’, while the other strand runs from 3’ → 5'
DNA Directionality
DNA polymerases replicate DNA by moving along a template strand and synthesising a new complementary strand
-
DNA polymerases add new nucleotides by joining the 5’-end of a new nucleotide to the 3’-end of the existing chain
-
Hence DNA is synthesised in a 5’ → 3’ direction, as the 3’-terminal is the end that is being extended
Because double stranded DNA is antiparallel, this means that the extension of the two new strands will occur in opposite directions




