Diploid vs Haploid
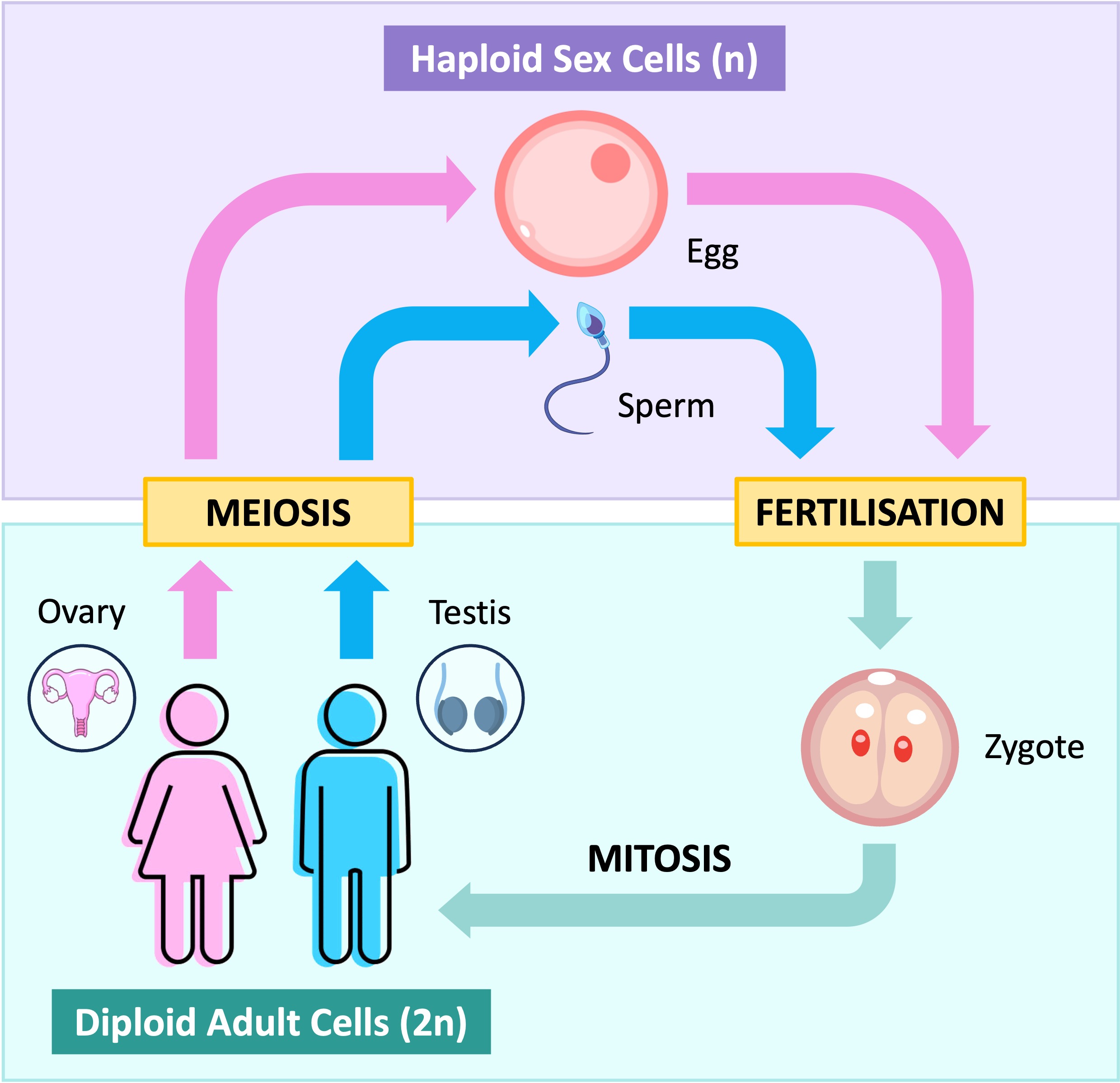
Most sexually reproducing organisms are diploid, meaning they have two copies of every chromosome (one maternal copy and one paternal copy)
-
With the exception of the sex chromosomes, these pairs are all homologous (they have the same genes at the same loci positions)
In order to reproduce, these organisms need to make gametes that are haploid (possessing only one copy of each chromosome)
-
Haploid gametes are produced from diploid germ cells via the process of meiotic nuclear division in the gonads
The fusion of two haploid gametes (egg + sperm) via fertilisation will result in the formation of a diploid zygote that can grow into a new organism via mitosis
-
If chromosome number was not halved in gametes, total chromosome numbers would double each generation (polyploidy)
Sexual Life Cycle