Dihybrid Crosses
A dihybrid cross determines the genotypic and phenotypic combinations of offspring for two particular genes that are unlinked
-
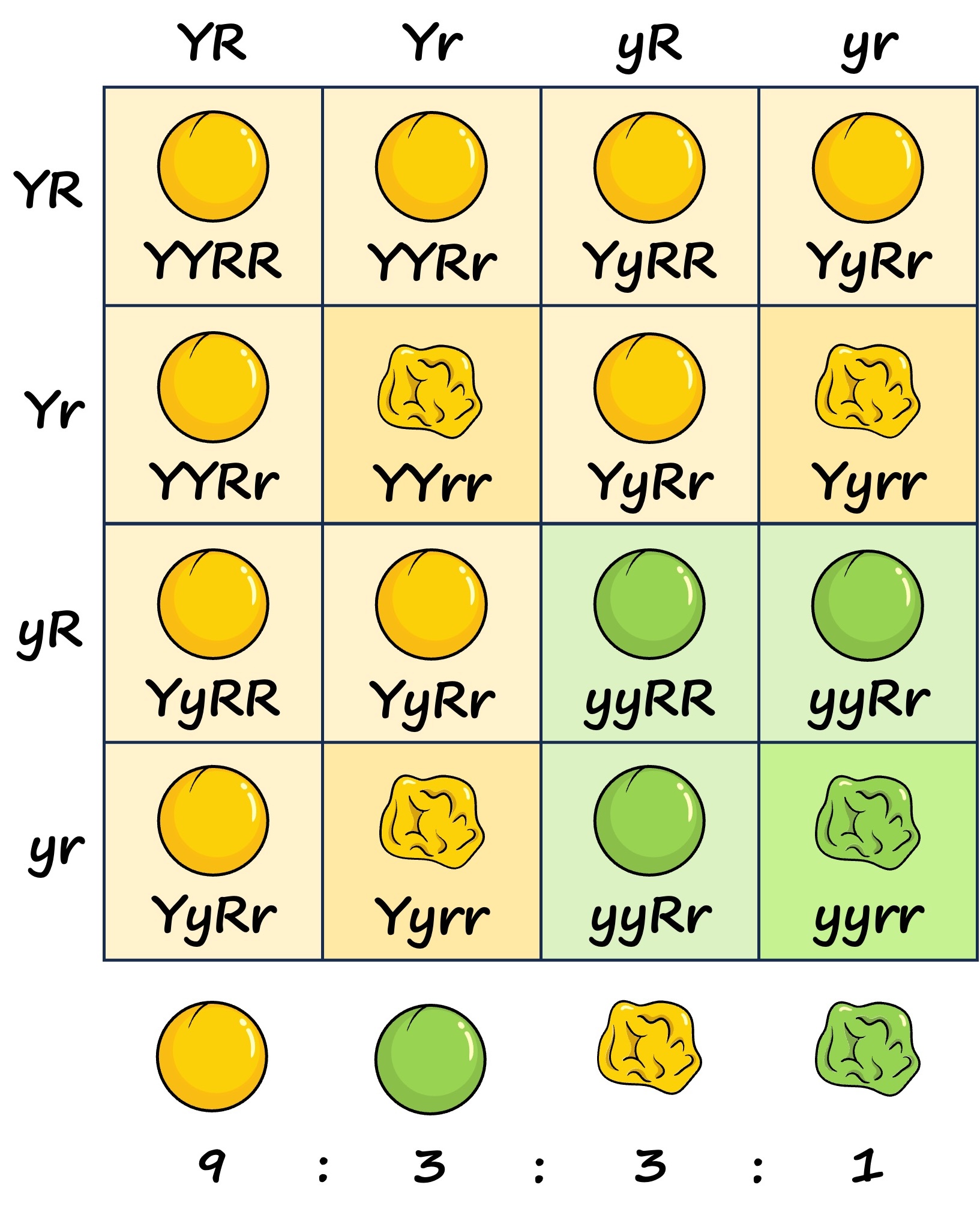
Because there are two genes, each with two alleles, there can be up to four different gamete combinations
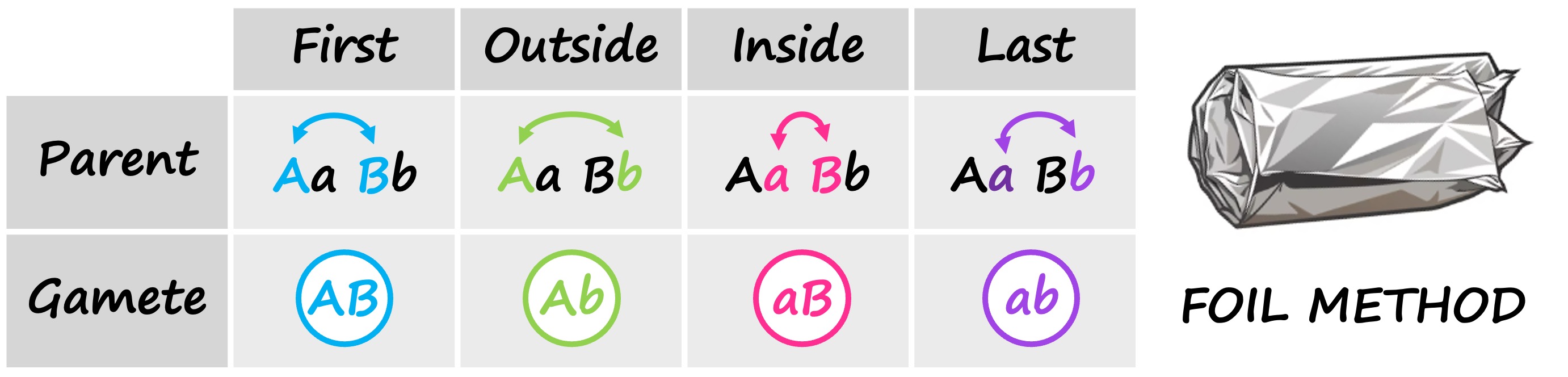
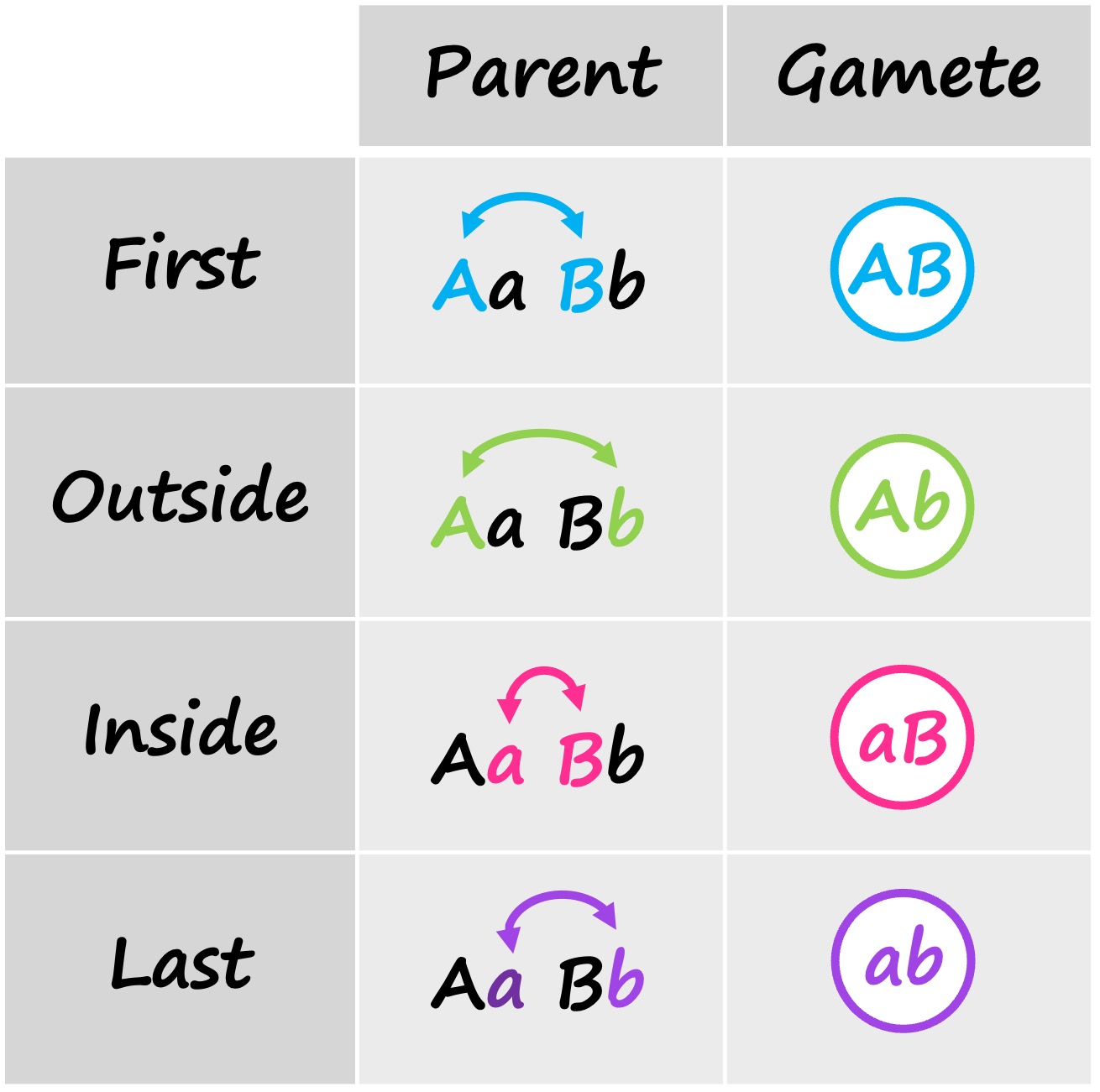
The easiest way to work out potential gamete combinations in a dihybrid cross is to use the FOIL method:
-
FOIL = First / Outside / Inside / Last
Completing Dihybrid Crosses
The inheritance of dihybrid traits can be calculated according to the following steps:
-
Designate characters to represent the alleles
-
A capital letter is used for the dominant allele, lower case letter for the recessive allele
-
-
Write down the genotype and phenotype of the parents (P generation)
-
Always pair alleles from the same gene and always write capitals first (e.g. AaBb, not ABab)
-
-
Identify all potential gamete combinations for both parents
-
Use the FOIL method to identify all possible combinations
-
-
Use a Punnett square to work out potential genotypes of offspring
-
Only include different gamete combinations for each parent (e.g. AaBB has only two combinations = AB and aB)
-
-
Write out the phenotype ratios of potential offspring
-
Phenotypic ratios reflect mathematical probabilities only and may not necessarily reflect actual offspring ratios
-
Dihybrid Cross (YyRr × YyRr)