Differentiation
Differentiation is the process during development whereby newly formed cells become more specialised and distinct from one another as they mature
-
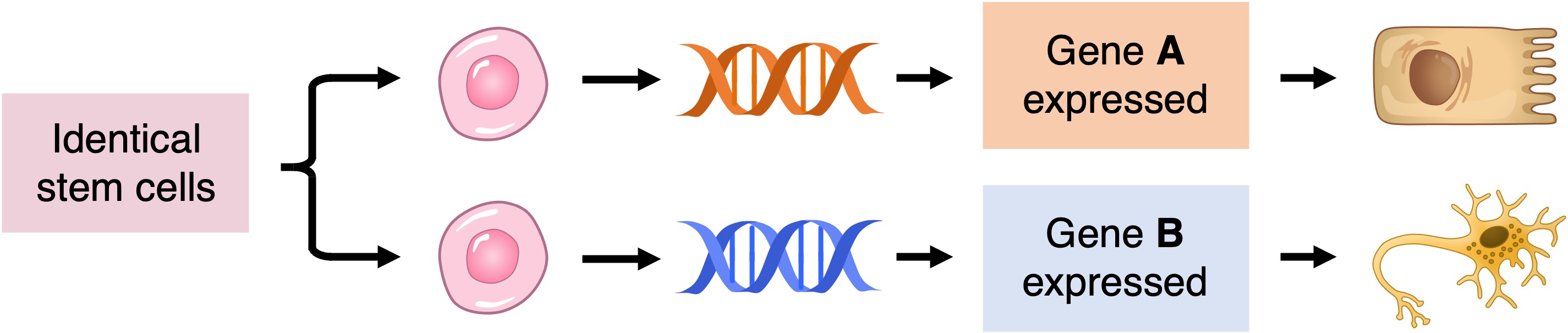
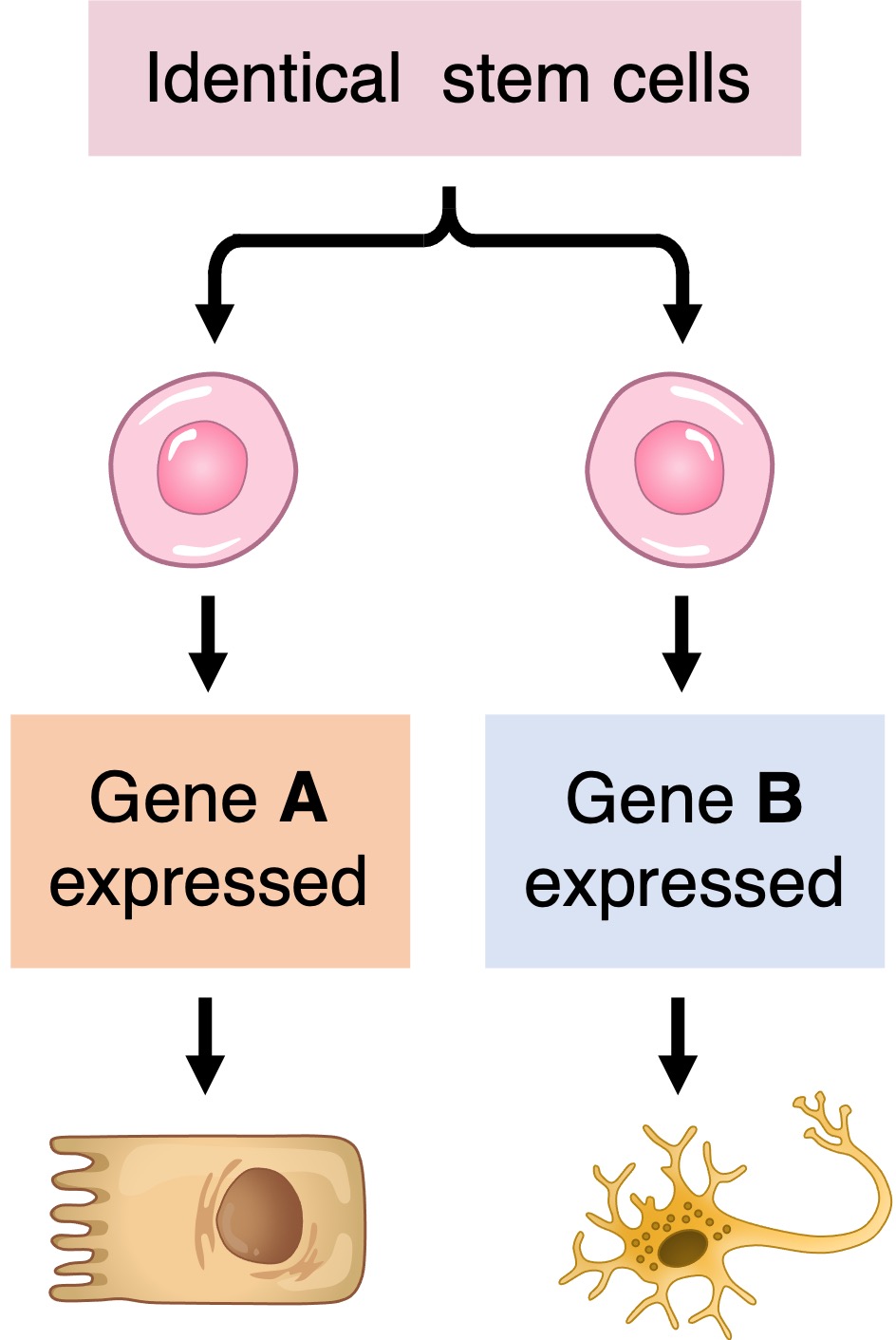
All cells of a multicellular organism share an identical genome – each cell contains the entire set of genetic instructions for that organism
-
The activation of different instructions (genes) within a given cell by chemical signals will cause it to differentiate into different cell types
Differential Gene Expression
Embryonic Development
Following fertilisation, an unspecialised zygote will divide and develop into a mass of specialised cells (early embryo) via differentiation
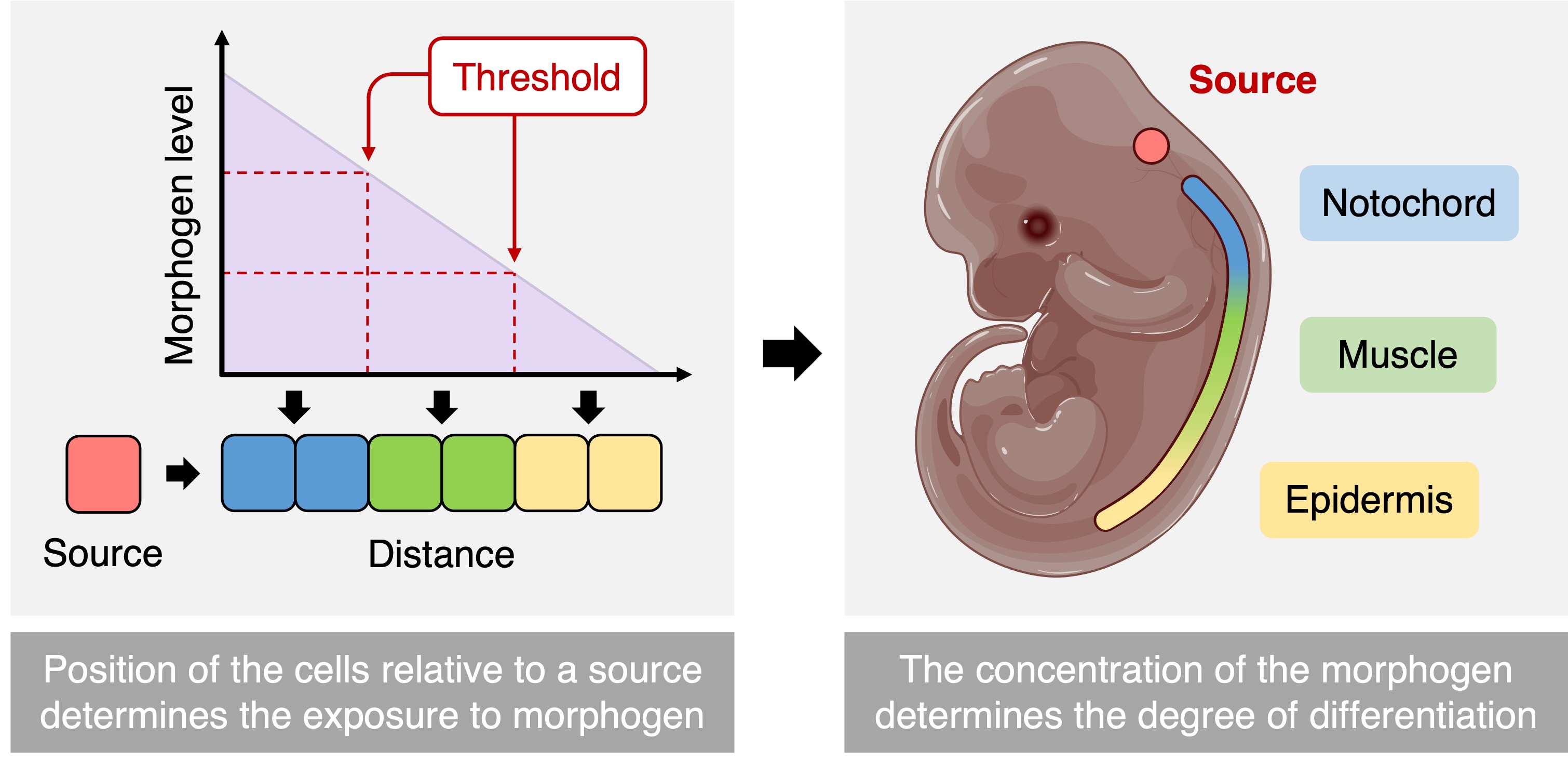
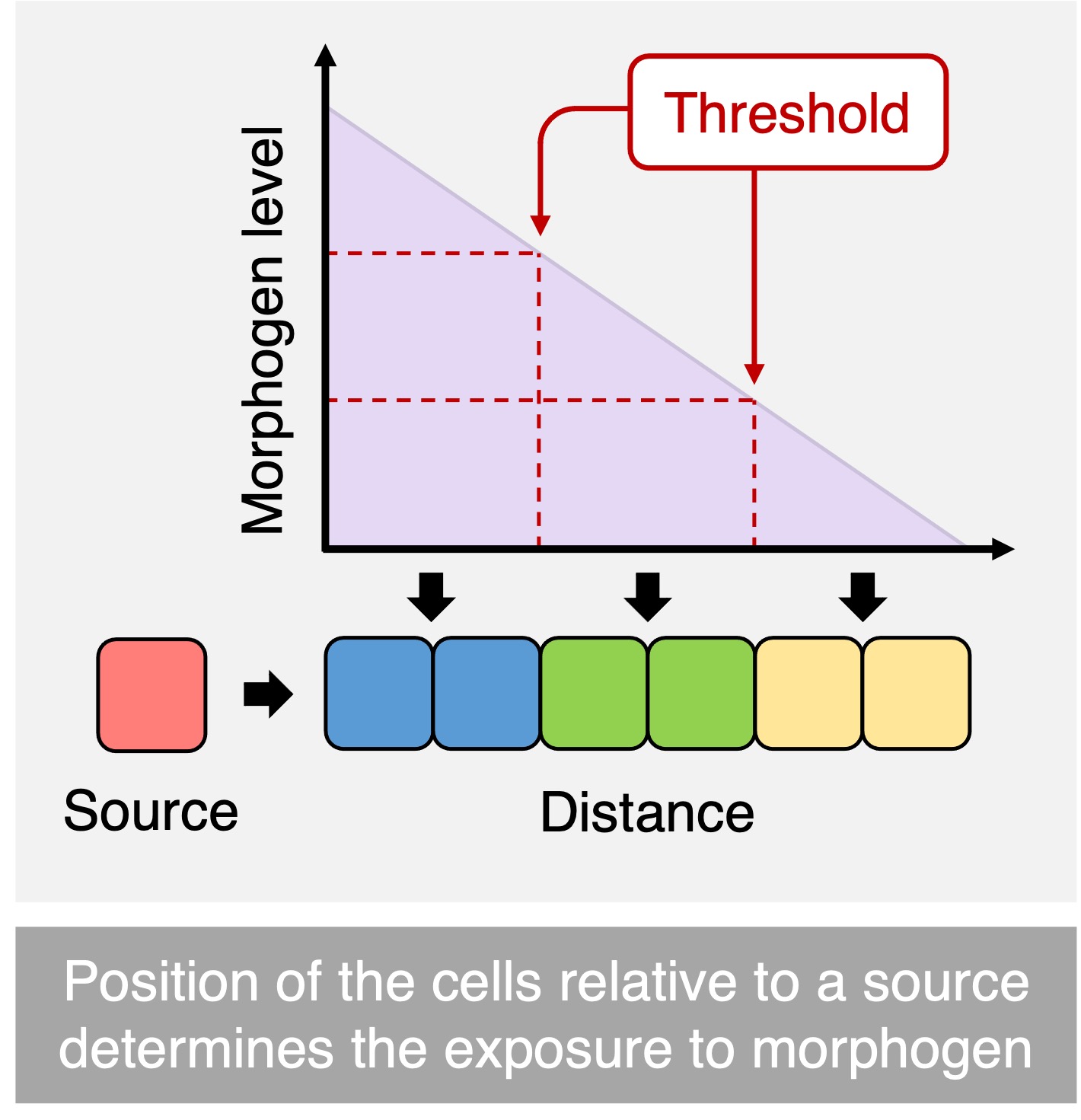
This process is driven by the release of gene regulating chemicals (transcription factors) called morphogens
-
The impact of the morphogen will be determined by its relative concentration (which decreases as the morphogen diffuses from the source cell)
-
Cells closer to the morphogen source receive higher concentrations of morphogen, resulting in the activation of more genes
-
Cells further away from the morphogen source receive lower concentrations of morphogen, resulting in the expression of fewer genes
Hence morphogen gradients control the differential expression of genes within an early-stage embryo
Morphogen Gradients