
Coordination
Multicellullar organisms are capable of completing functions that unicellular organisms could not undertake – this is due to the collective actions of individual cells combining to create new synergistic effects
-
These emergent properties arise when the interaction between individual components produce new functionalities
In multicellular organisms:
-
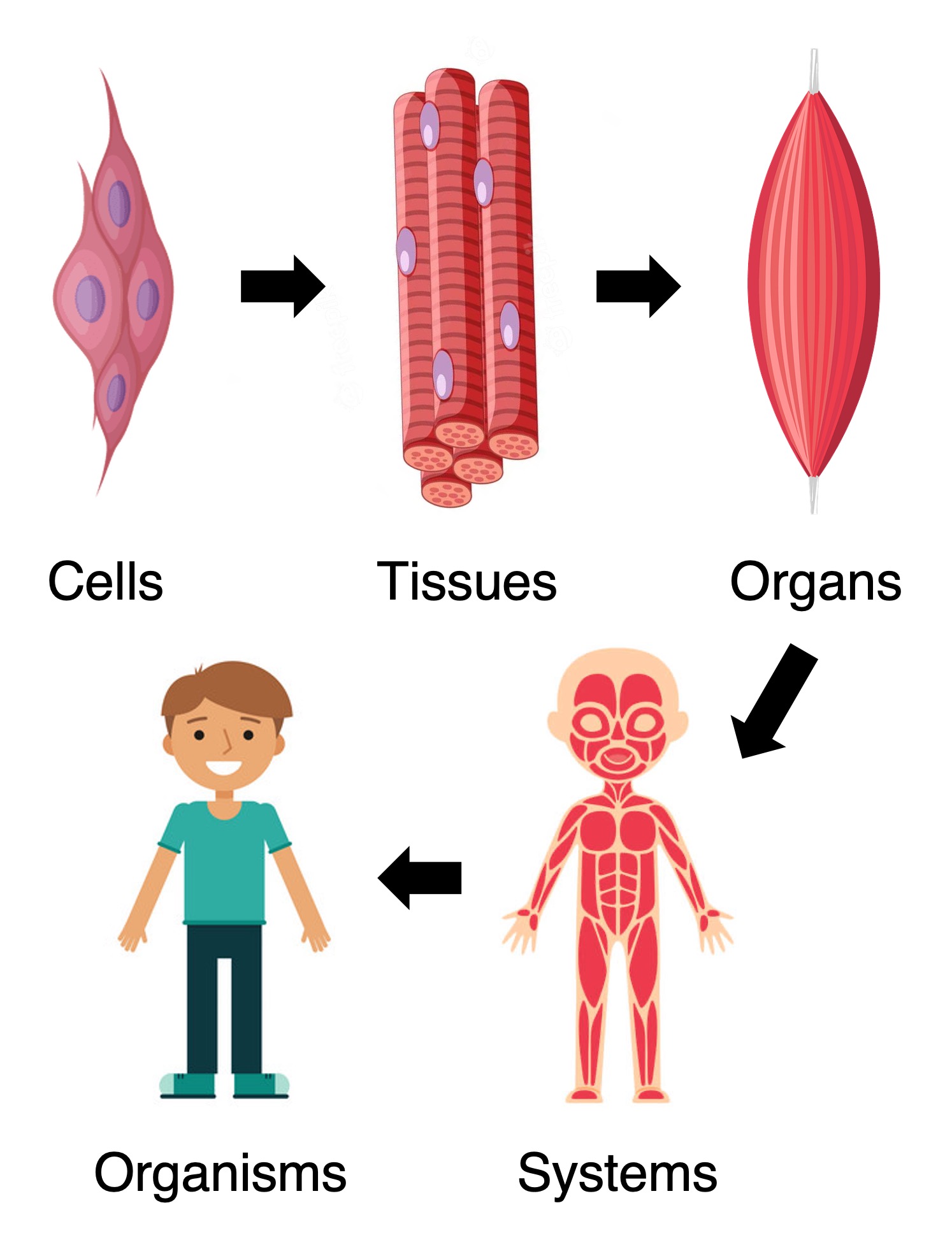
Cells of the same type may be grouped together to form tissues
-
The functional grouping of multiple tissues results in the formation of organs
-
Organs may interact to form organ systems capable of carrying out specific body functions
-
Organ systems collectively carry out the life functions of the complete organism
Systems Organisation

Systems Integration
Coordination of the different organ systems is required to allow multicellular organisms to collectively perform the functions of life
-
Each component part contributes essential functionality to the organism and interacts with other components to meet the requirements for survival
Examples of core organ systems in multicellular animals include:
-
Respiratory system – Mediates the exchange of gases between the organism and the environment
-
Cardiovascular system – Facilitates the movement of materials between the different body systems
-
Nervous system – Acts as a rapid communication system via the transfer of electrical signals
-
Endocrine system – Releases chemical signals as part of a widely distributed communication network
-
Lymphatic system – Contributes towards the development of immunity against foreign pathogens
-
Excretory system – Removes from the body the toxic waste products of metabolic reactions
-
Musculoskeletal system – Provides a structural framework and means of locomotion (movement)
-
Reproductive system – Allows for the successive production of new generations of organisms
Systems Organisation





