Communication
Animals possess two distinct communication systems which allow for coordination between body organs – the nervous system and the endocrine system
-
These two systems are interconnected but differ in their mechanism of action and consequently serve different functions within the organism
Nervous System
-
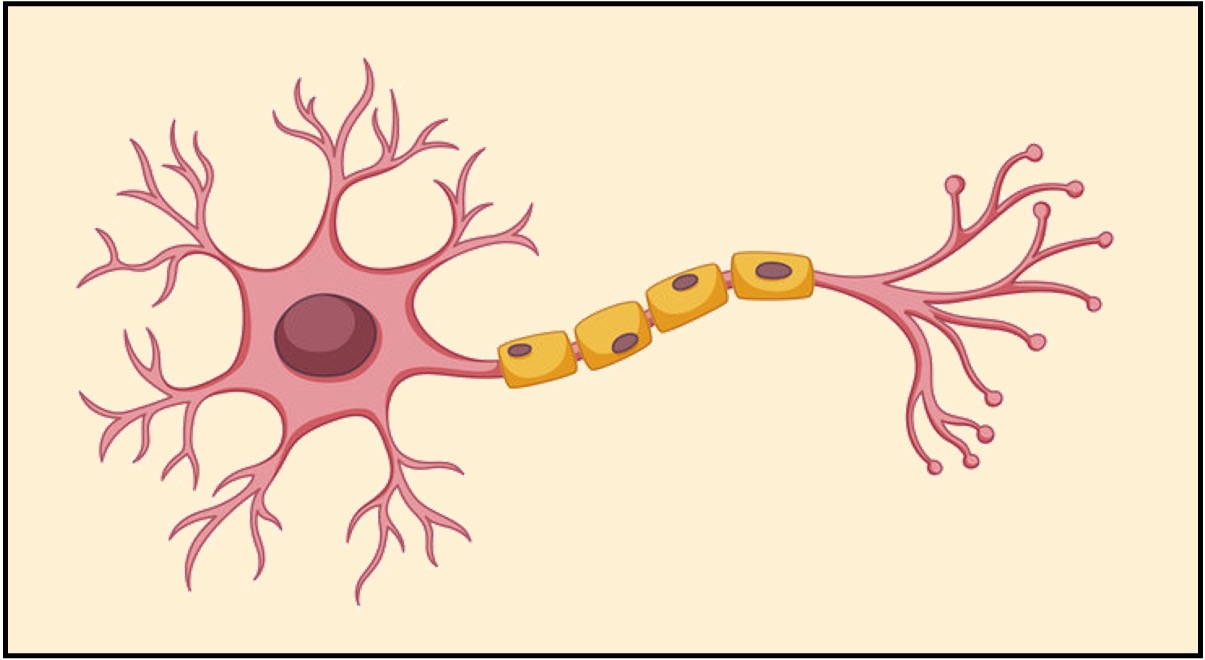
Consists of a network of nerve cells (neurons) that transmit electrochemical impulses (faster signalling)
-
The nerve signals are transmitted to specific localised targets and have a short duration of effect
-
This network is composed of a central nervous system (CNS) and a peripheral nervous system (PNS)
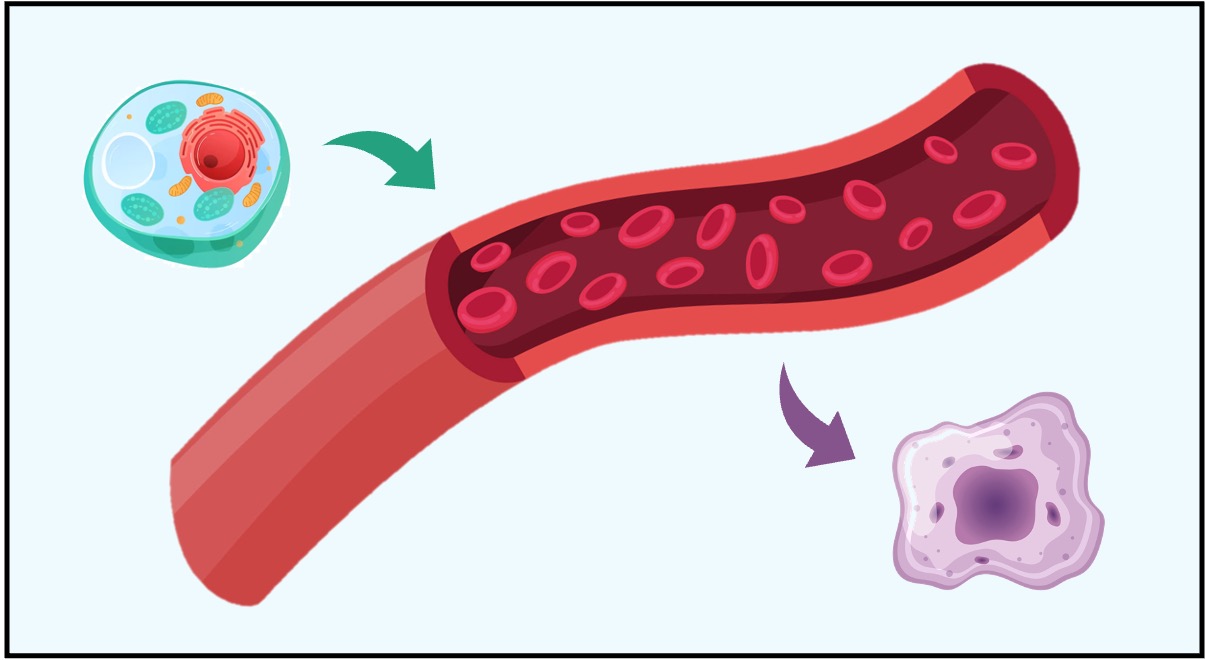
Endocrine System
-
Consists of ductless endocrine glands that release chemical messengers (hormones) into the bloodstream
-
The hormones act on distant target cells, allowing for a wider distribution and longer duration of effect
-
The hypothalamus is the section of the brain that acts as a link between the nervous and endocrine systems
Communication Systems
Nervous System