Coenzymes
Coenzymes are non-protein organic compounds that facilitate enzyme reactions by cycling between a loaded and unloaded form
-
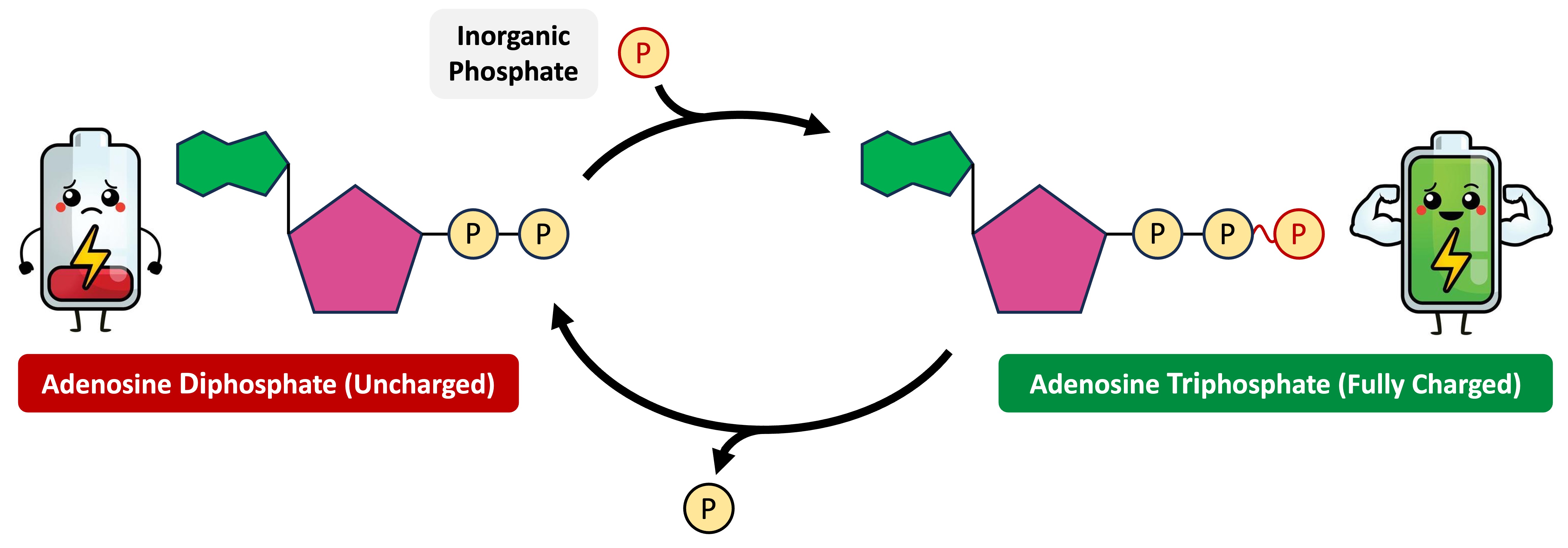
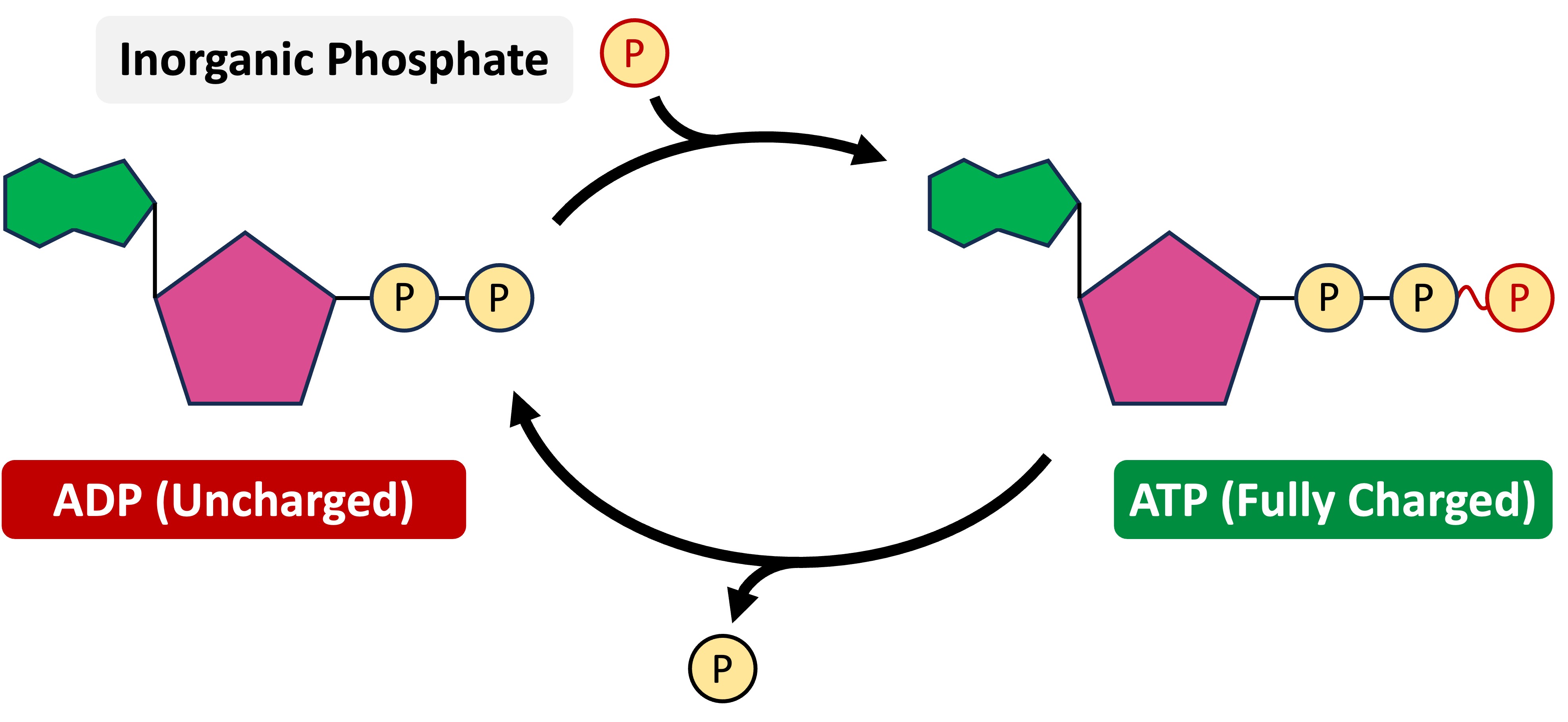
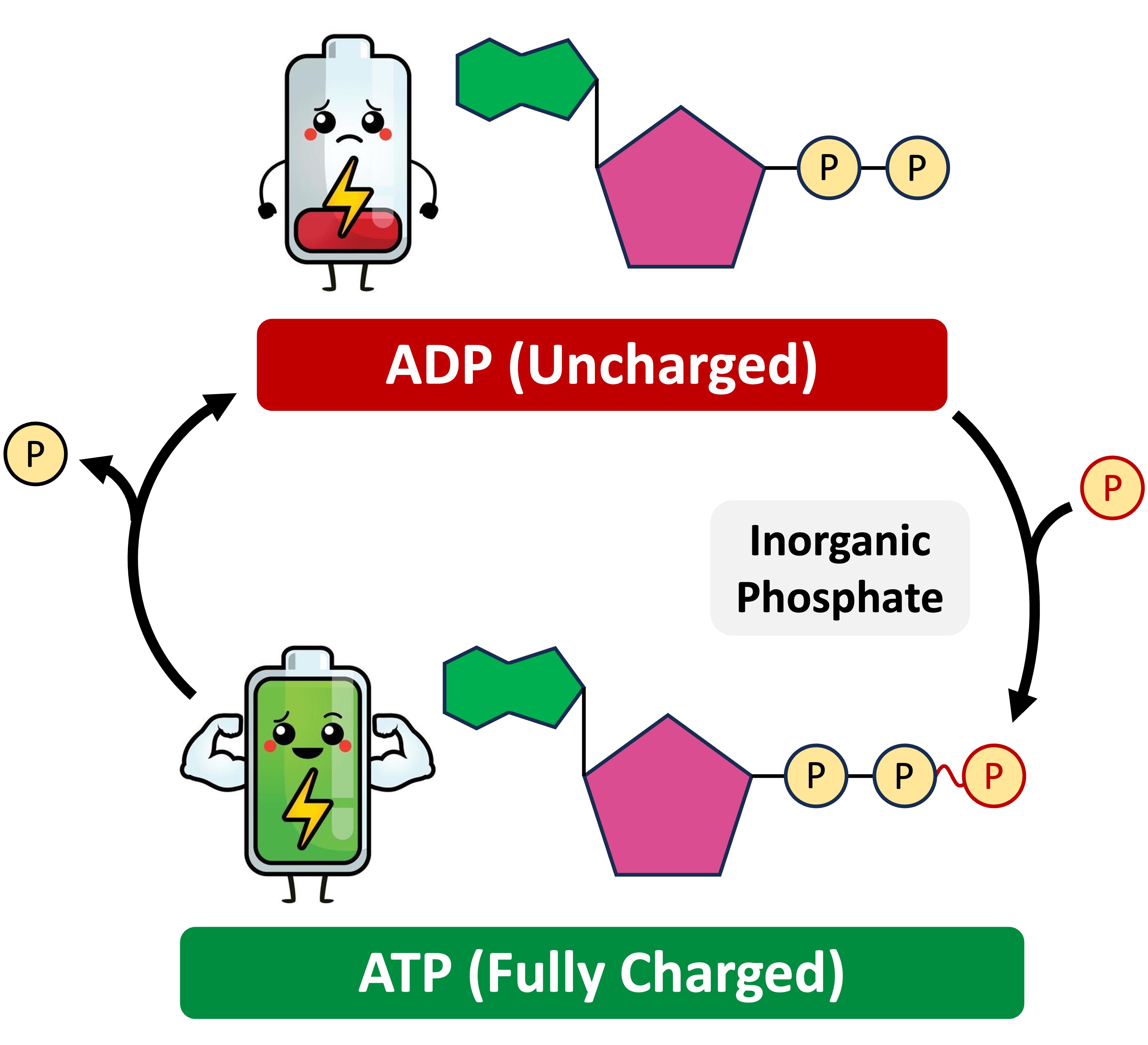
ATP is a loaded coenzyme that transfers chemical energy to enzymes and enables the activation energy threshold to be reached (triggering catalysis)
ATP stores chemical energy in the covalent bonds between the phosphate groups (phosphates are negatively charged and hence require high amounts of energy to keep in place)
-
When ATP is hydrolysed, the terminal phosphate is released and the coenzyme is converted to its unloaded form (ADP = adenosine diphosphate)
-
The chemical energy released by ATP hydrolysis is used by an enzyme to catalyse a metabolic reaction within the cell
Energy Transfer (ATP ↔ ADP)