Cholesterol
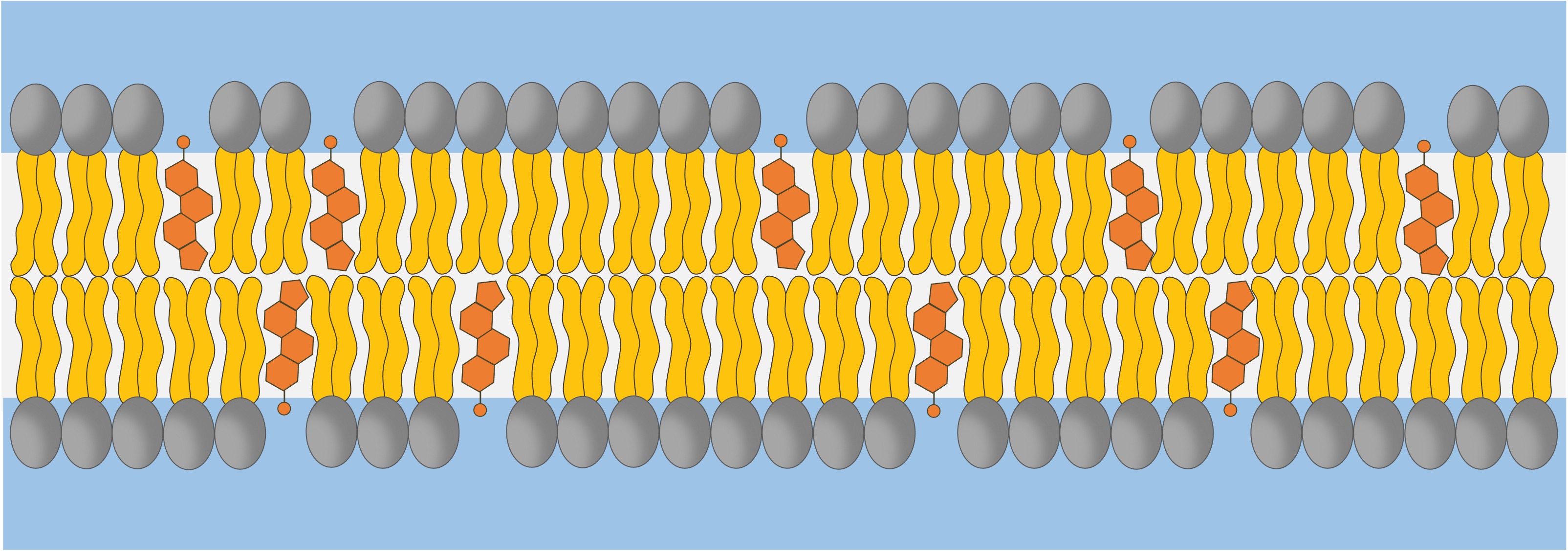
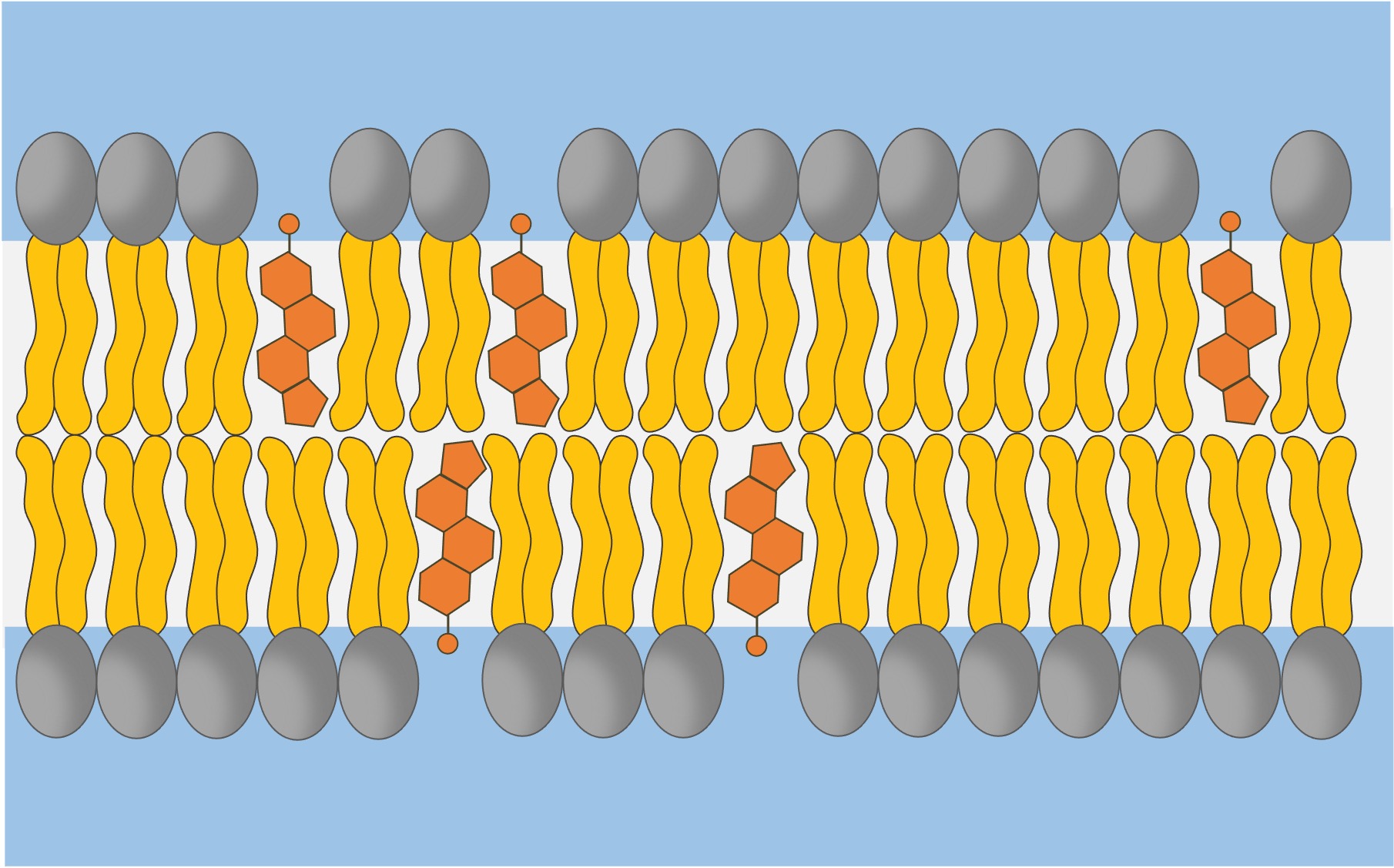
Cholesterol is a sterol (ringed) lipid that plays an important role in regulating fluidity in animal cell membranes
-
Organisms with cell walls lack cholesterol in their membranes, but plants and fungi may contain related compounds that perform comparable functions
Cholesterol is an amphipathic molecule and is located within the phospholipid bilayer
-
The hydrophilic hydroxyl group associates with the phosphate heads, while the hydrophobic carbon rings sit between the fatty acid tails
Within the plasma membrane, cholesterol acts as a bidirectional modulator (adjustor) of membrane fluidity
-
At high temperatures it functions to stabilise the membrane and raises the melting point (lowering fluidity)
-
At low temperatures it intercalates between the phospholipids, preventing stiffening and crystallisation (raising fluidity)
Cholesterol also fulfils certain functional roles within a plasma membrane
-
It makes the membrane less permeable to very small water-soluble molecules that would otherwise freely cross
-
It helps secure peripheral proteins by forming high density lipid rafts capable of anchoring the protein
Cholesterol in Membranes