
Cell Structure
There are four basic structures common to all cells:
-
Plasma Membrane – All cells must have an outer border to maintain an internal chemistry that is different to the exterior (homeostasis)
-
Genetic Material – All cells must contain coded instructions (DNA) that function to control internal activities within a cell (metabolism)
-
Ribosomes – All cells must contain ribosomes in order to translate the cell’s coded instructions into functional elements (proteins)
-
Cytosol – All cells must contain an internal fluid that functions as a reaction medium for all necessary metabolic processes
Atypical Structures
Certain types of eukaryotic cells and tissues do not conform to the standard organisation of a typical cell
-
These cells have developed unique characteristics in order to better to support their specific cellular activities
Striated Muscle Fibres:
-
Individual muscle cells fuse together to form long striated muscle fibres
-
These fibres are surrounded by a continuous plasma membrane and possess multiple nuclei
-
Striated muscle fibres challenge the idea that all living things are comprised of discrete cell units
Aseptate Fungal Hyphae:
-
Fungi may have filamentous structures called hyphae, which are used for nutrient absorption and growth
-
Hyphal cells are typically separated by internal walls (septa), but some hyphae are not partitioned and have a continuous cytoplasm (with multiple nuclei)
-
Aseptate fungal hyphae challenge the idea that living structures are composed of autonomous cells
Sieve Tube Elements:
-
Sieve elements that line the phloem in plants are interconnected by plasmodesmata into supracellular assemblies that transverse the length of a plant
-
These sieve elements also lack nuclei and have few organelles, relying on local companion cells for survival
-
Phloem sieve tube elements challenge the idea that multicellular structures are composed of anatomically independent cells
Red Blood Cells:
-
Red blood cells have no nucleus or mitochondria when they are mature (the organelles are ejected to allow more haemoglobin to be stored)
-
Without any genetic material, red blood cells cannot independently replicate and new cells must be continually produced within the bone marrow
-
Red blood cells challenge the traditional definition of a eukaryotic cell as they lack critical structures needed for autonomous survival
Atypical Cell Structures
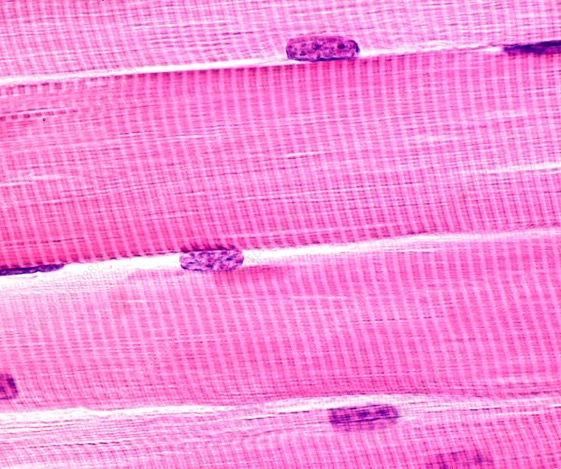

Skeletal Muscle
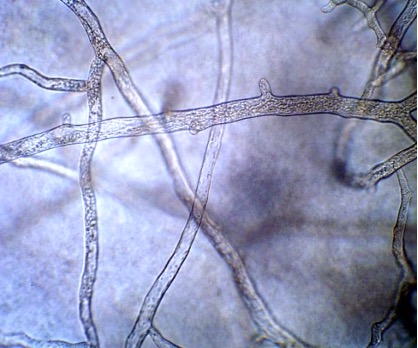
Fungal Hyphae
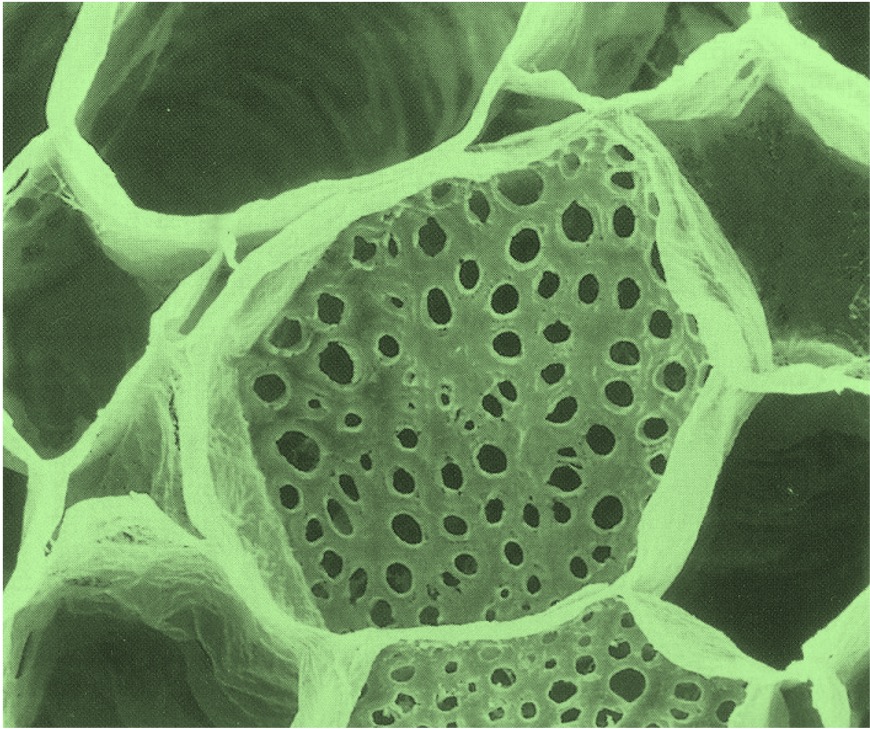
Sieve Element
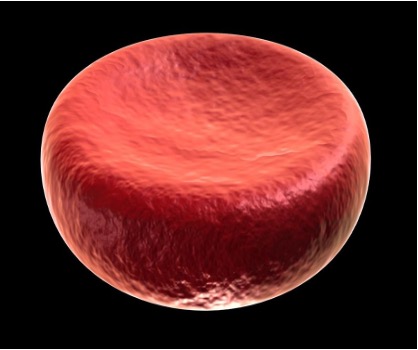
Red Blood Cell




