Cell Respiration
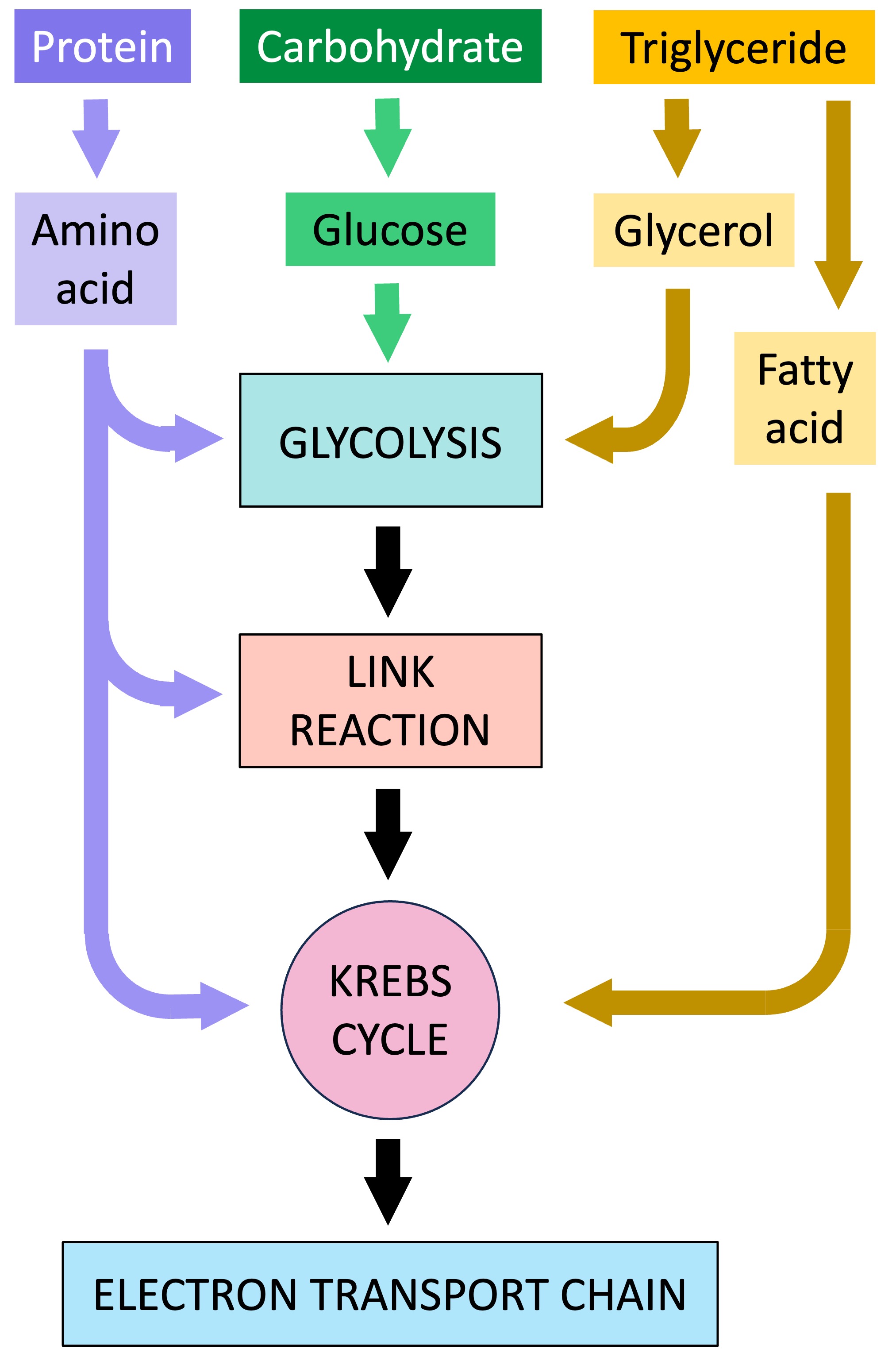
Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from the breakdown of organic compounds to produce ATP
-
ATP is produced from ADP as a consequence of the transfer of chemical energy from the digested carbon compound
The main organic compound used for this process is carbohydrates (glucose), although lipids and proteins can also be digested
-
Lipids (fatty acids) produce more energy per gram, however are harder to digest and transport
-
Proteins (amino acids) can produce a comparable amount of energy to carbohydrates, but also produce toxic nitrogenous wastes (NH3)
Energy Sources