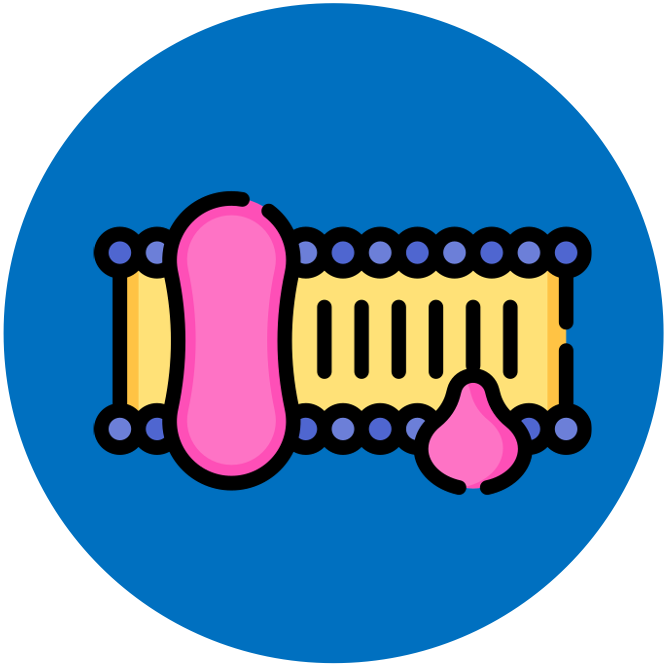
Cell Membranes
Cell membranes function to enclose the contents of the cell, separating the intracellular components from the external environment
-
This allows for the control of internal conditions within the cell and the maintenance of homeostasis
Cell membranes possess two key qualities that function to promote homeostatic regulation:
-
Semi-permeability: Only certain materials are able to freely cross the cell membrane
-
Selectivity: The cell can control the passage of any material that cannot freely cross the membrane
Cell membranes are comprised of two main components: phospholipids and proteins
Phospholipid Bilayer:
-
The phospholipids form a bilayer that acts as a barrier to certain materials (i.e. it is semi-permeable)
-
The hydrocarbon chains that form the core of the bilayer are hydrophobic and have low permeability to large and charged substances
-
This means that large compounds and hydrophilic particles (ions and polar molecules) cannot cross the bilayer
Membrane Proteins:
-
Membrane proteins embedded within the phospholipid bilayer may act as points of transport for large and charged substances
-
This makes the lipid bilayer a selective barrier as the membrane proteins can coordinate the transport of hydrophilic materials according to need