Cell Division
Reproduction is a function of life and involves the formation of new cells from a progenitor source (a ‘parent’ cell)
-
This cell division produces new ‘daughter’ cells that can form multicellular tissues or entirely new organisms
-
All cells undergo cell division in order to reproduce (as per the cell theory: all cells arise from pre-existing cells)
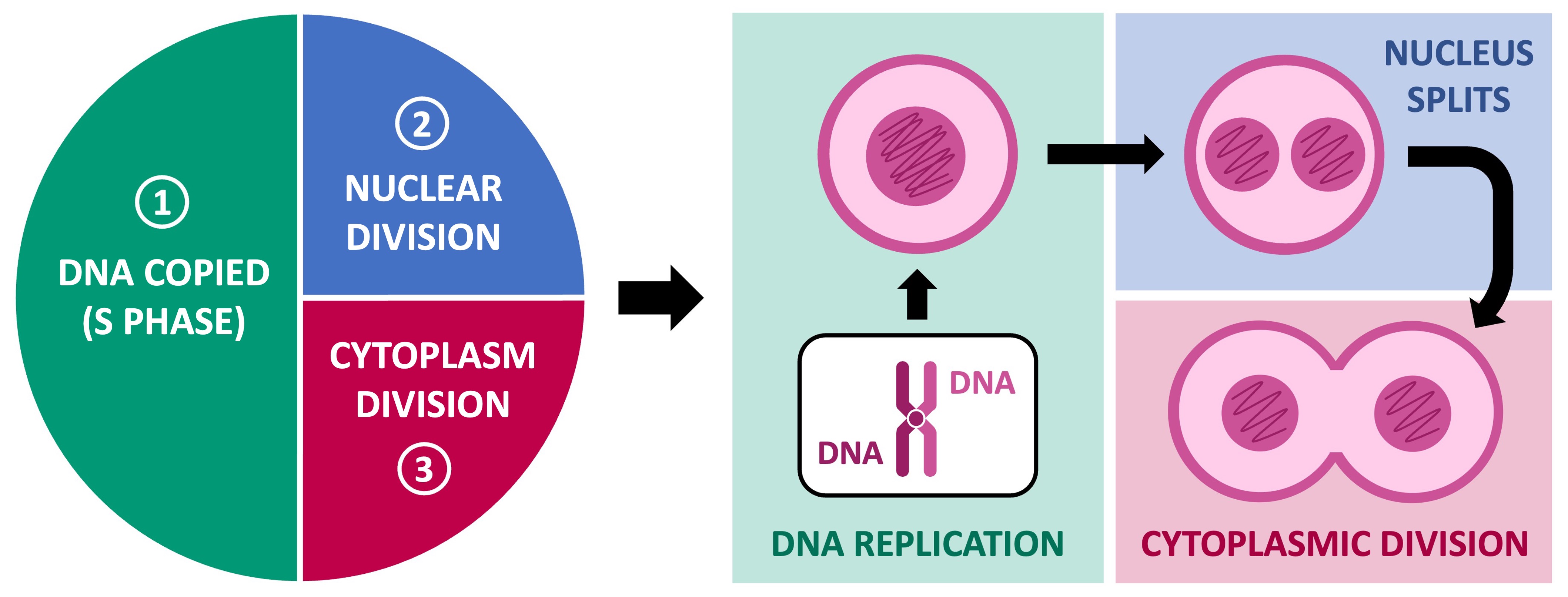
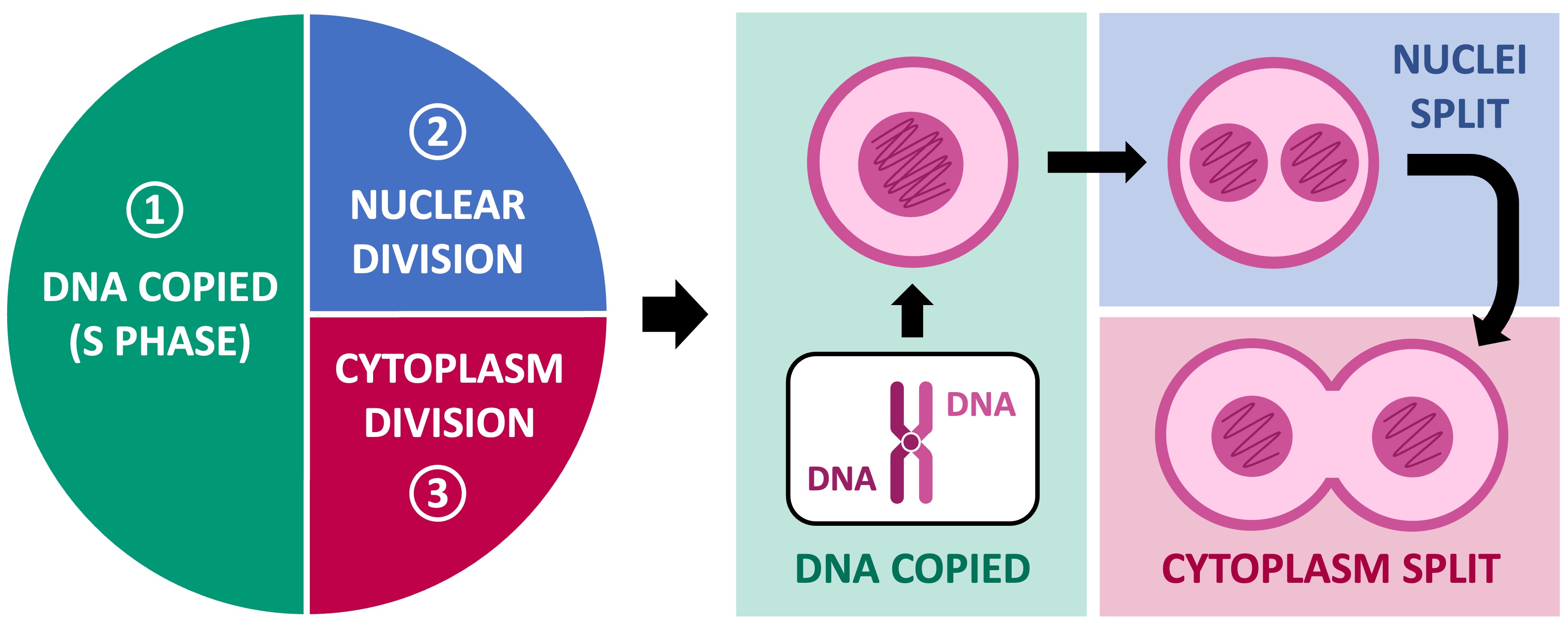
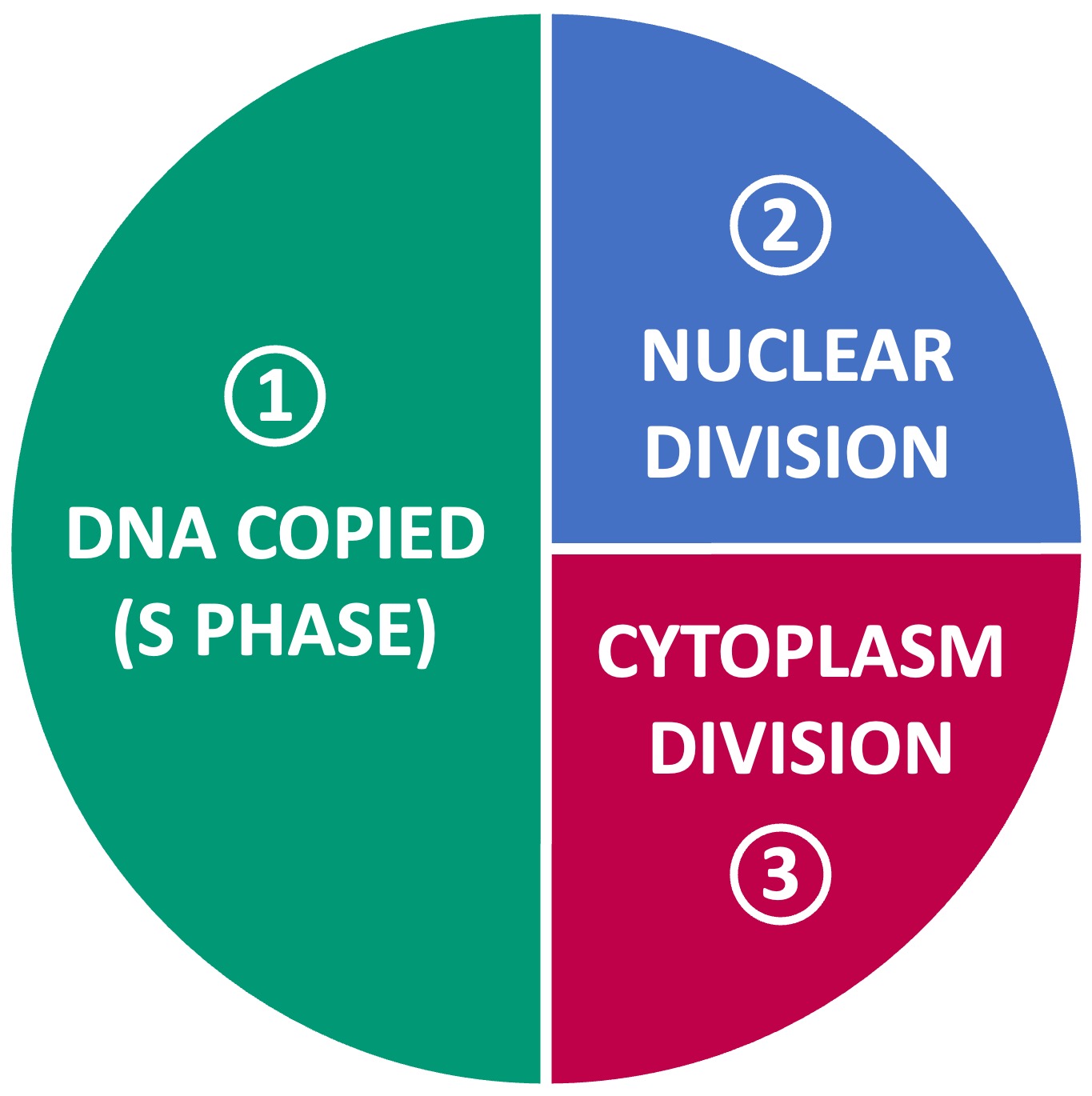
In eukaryotes, the process of cell division involves three basic stages:
-
DNA Replication: The genetic material of the cell is first duplicated (this occurs during the S phase of interphase)
-
Nuclear Division: The DNA is separated into two nuclei (one nucleus for each eventual daughter cell)
-
Mitosis is a process of nuclear division that maintains a constant chromosome number in daughter nuclei (asexual reproduction)
-
Meiosis is a process of nuclear division that halves the chromosome number in daughter nuclei (for sexual reproduction)
-
-
Cytokinesis: Finally, the cytoplasm is divided to produce two individual daughter cells
As prokaryotes lack a nucleus, neither mitosis or meiosis occurs in these cells (bacteria reproduce asexually via binary fission)
Process of Cell Division