Calvin Cycle
The light independent reactions use the chemical energy derived from light dependent reactions to form organic molecules
-
The light independent reactions occur in the fluid-filled space of the chloroplast called the stroma
Step 1: Carbon Fixation
-
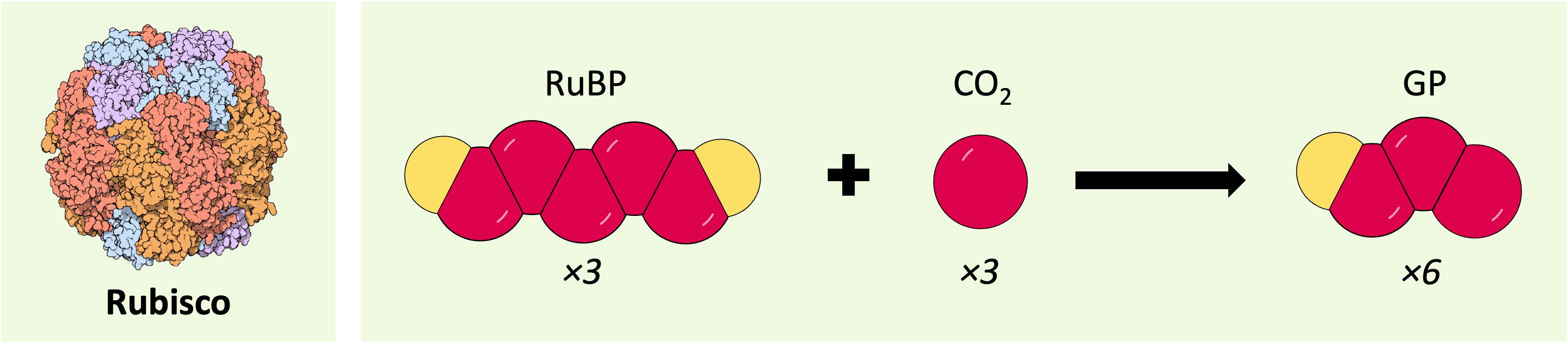
The Calvin cycle begins with a 5C compound called ribulose bisphosphate (or RuBP)
-
An enzyme, RuBP carboxylase (or Rubisco), catalyses the attachment of a CO2 molecule to RuBP
-
The resulting 6C compound is unstable, and breaks down into two 3C compounds – called glycerate-3-phosphate (GP)
-
A single cycle involves three molecules of RuBP combining with three molecules of CO2 to make six molecules of GP

Step 2: Reduction of G-3-P
-
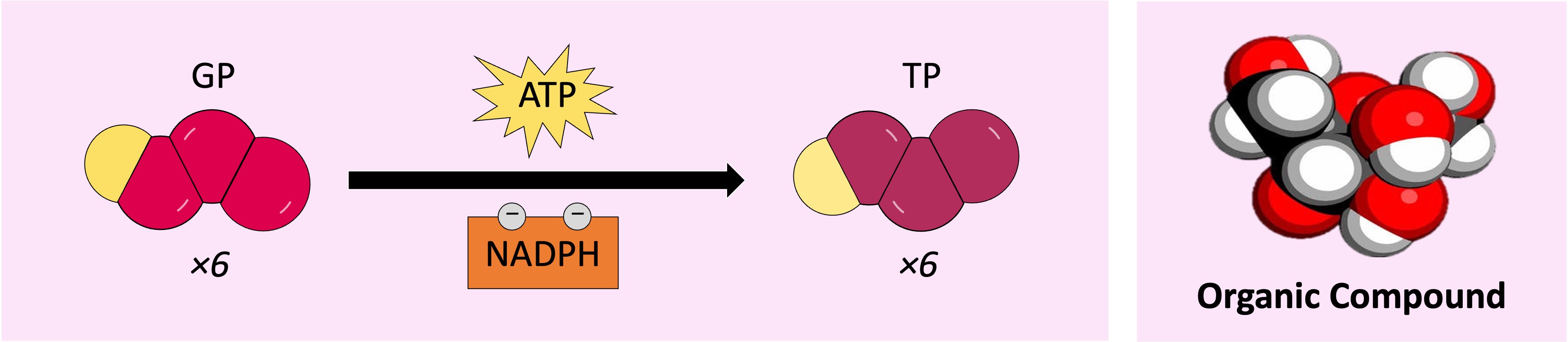
Glycerate-3-phosphate (GP) is converted into triose phosphate (TP) using NADPH and ATP
-
The NADPH and ATP are generated by the light dependent reactions (via non-cyclic photophosphorylation)
-
Reduction by NADPH transfers hydrogen atoms to the compound, while the hydrolysis of ATP provides energy
-
As six molecules of GP were produced via carbon fixation, six molecules of TP are similarly produced per cycle

Step 3: Regeneration of RuBP
-
Of the six molecules of TP produced per cycle, one TP molecule may be used to form half a sugar molecule
-
Hence two cycles are required to produce a single glucose monomer, and more to produce polysaccharides like starch
-
The remaining five TP molecules are recombined to regenerate stocks of RuBP (5 × 3C = 3 × 5C)
-
The regeneration of RuBP requires energy derived from the hydrolysis of ATP