Blood Vessels
The vascular system is comprised of blood vessels which function to circulate essential materials around the body
-
Materials that are transported within the bloodstream include nutrients (e.g. glucose), hormones, antibodies, respiratory gases (O2 and CO2) and waste products (e.g. urea)
-
The vascular system is also involved in regulating blood pressure and body temperatures (via vasodilation and vasoconstriction)
Blood Network
Blood is circulated by means of a muscular pump (the heart) and is transported within three main types of vessels
-
Arteries transport blood away from the heart at high pressure and branch to form smaller vessels (arterioles) that connect to capillaries
-
Capillaries are microvessels that function as the site of material exchange between the blood and the tissues
-
Veins transport blood towards the heart at low pressure and are formed from smaller vessels (venules) that arise from the convergence of capillaries
Blood Circulation

Vessel Comparison
The difference in the structural characteristics of arteries, capillaries and veins is attributable to their respective functions
-
Arteries have thick walls and narrow lumens because they transport blood at high pressure
-
Capillaries have walls that are only a single cell thick because they exchange materials between blood and tissue
-
Veins have thin walls with wide lumens and valves because they transport blood at low pressure
-
Artery
Vein
Capillary
Function
Sends blood from the heart
Sends blood to the heart
Material exchange with the tissues
Pressure
High pressure
Low pressure
Very low pressure
-
Diameter
Narrow lumen
Wide lumen
Extremely narrow lumen
Vessel Wall
Thick wall
(3 layers)
Thin wall
(3 layers)
Very thin wall
(1 layer)
Elastic Fibres
Large amounts
Small amounts
None
Valves
No valves
Has valves
No valves
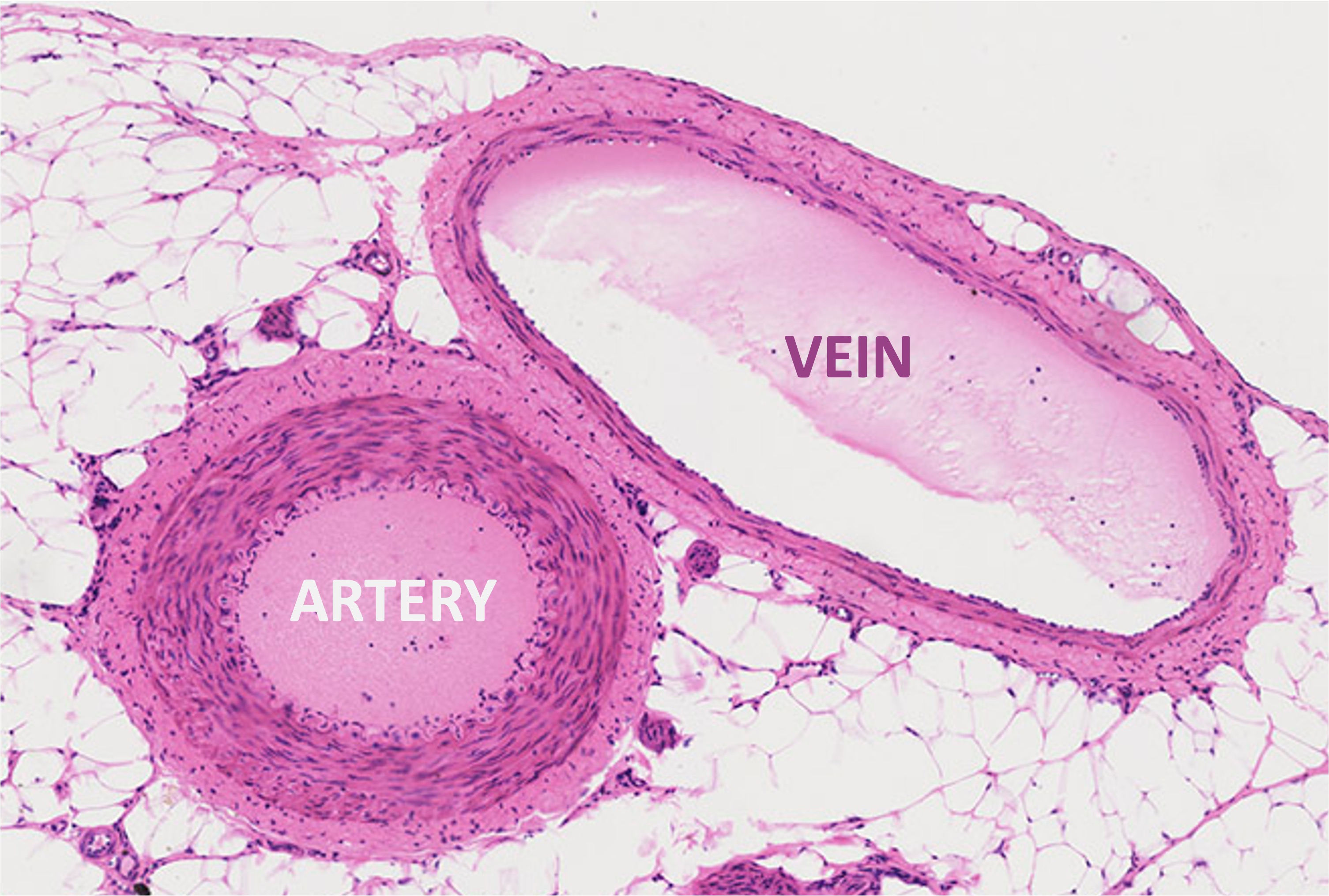
Vessel Identification
Blood vessels can be identified from histological slides or images according to the thickness of their walls and the diameter of their lumen:
-
Arteries have thick walls composed of three distinct layers (tunica), but their lumen are comparatively narrower than veins
-
Veins have thinner walls (also composed of three layers), but their lumen are much wider compared to arteries
-
Capillaries are very small and will not be easily detected under the same magnification as arteries and veins
Blood Vessel Histology