Blood Flow
Blood circulates around the body as a consequence of the rhythmic contraction of the heart
-
Each contraction (or ‘heart beat’) forces a wave of blood through the arteries which can be detected as a pulse
-
The pulse rate will therefore reflect the speed at which the heart beats, measured by the number of contractions per minute (or bpm)
Pulse rate can be affected by a number of conditions – including exercise, age, disease, temperature and emotional state
-
The pulse rate is increased by the sympathetic nervous system and decreased by parasympathetic stimulation
-
The pulse rate can also be increased hormonally via the action of adrenaline / epinephrine
The pulse rate can be measured by counting the number of pulses that occur over the course of one minute
-
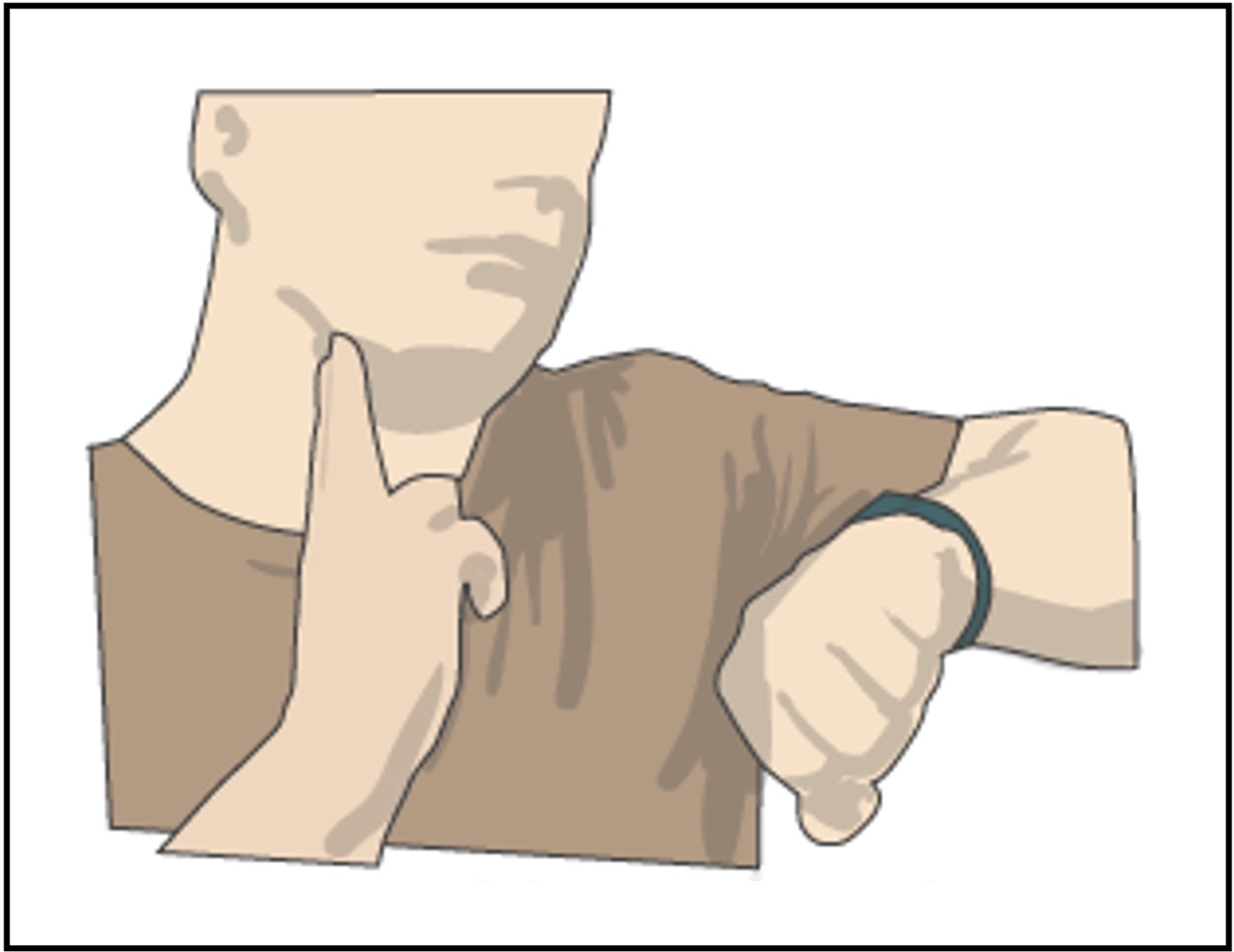
Measurements typically involve the carotid artery (neck) or the radial artery (wrist) – as these are locations where pulses are easiest to detect
Pulse Measurements
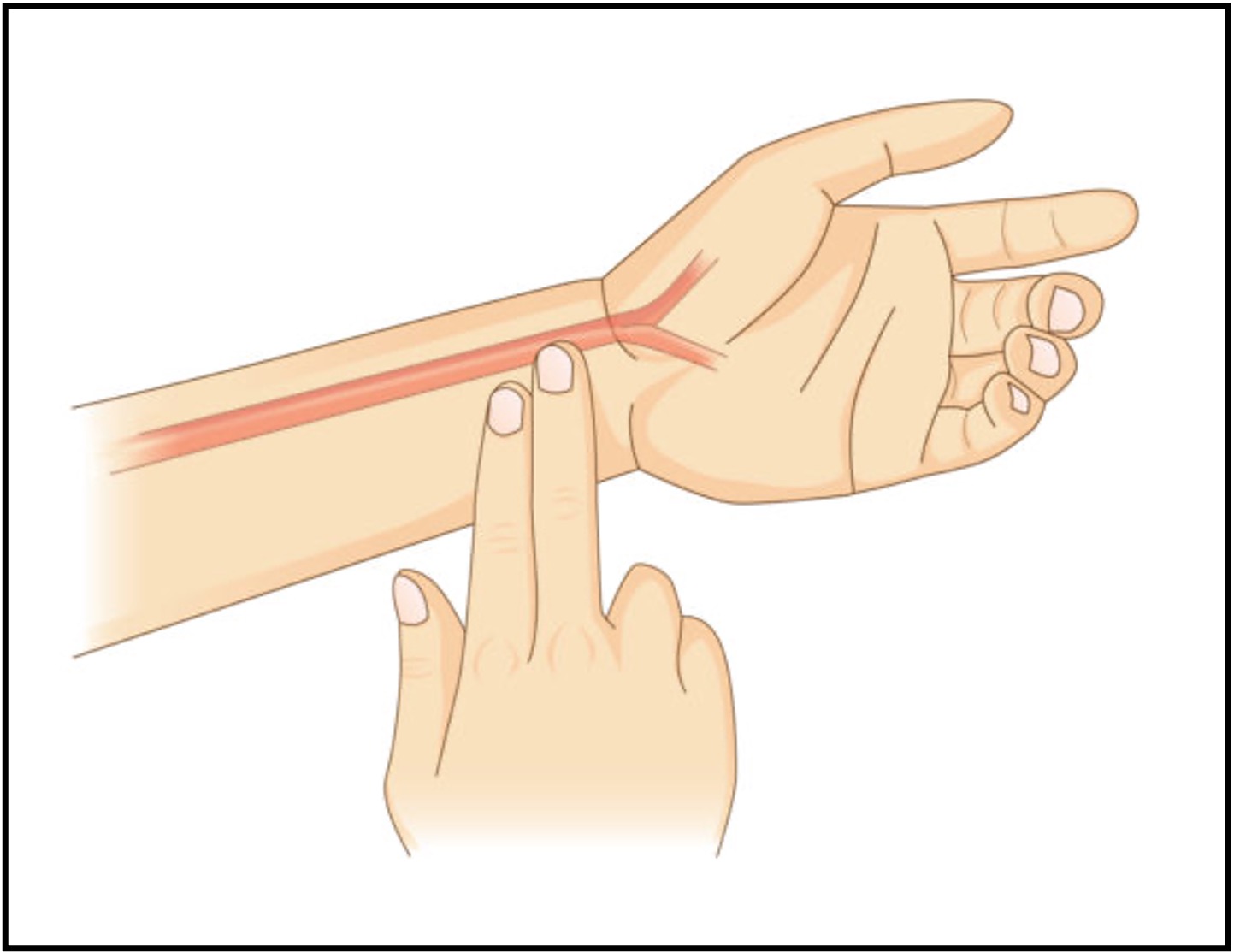
Radial Pulse