Base Sequence
Nucleic acids are composed of a combination of four nitrogenous bases
-
Guanine and adenine are double-ringed purine bases
-
Cytosine and thymine / uracil are single-ringed pyrimidine bases
Thymine and uracil are chemically similar molecules – thymine is used in DNA, while uracil is used in RNA
Nitrogenous Bases
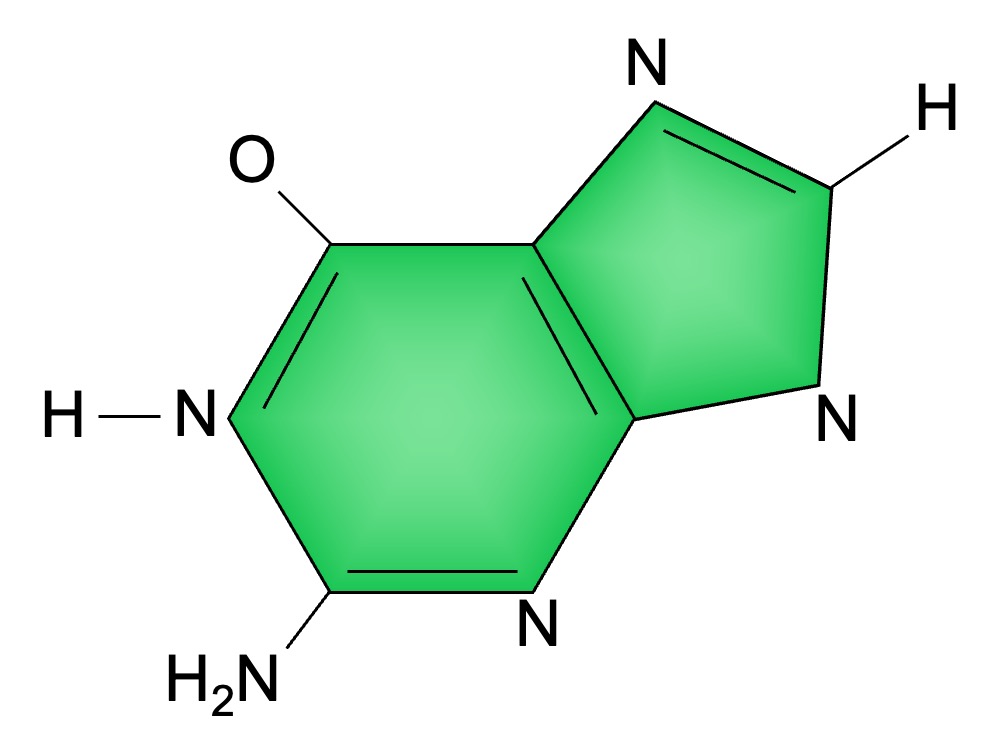
Guanine
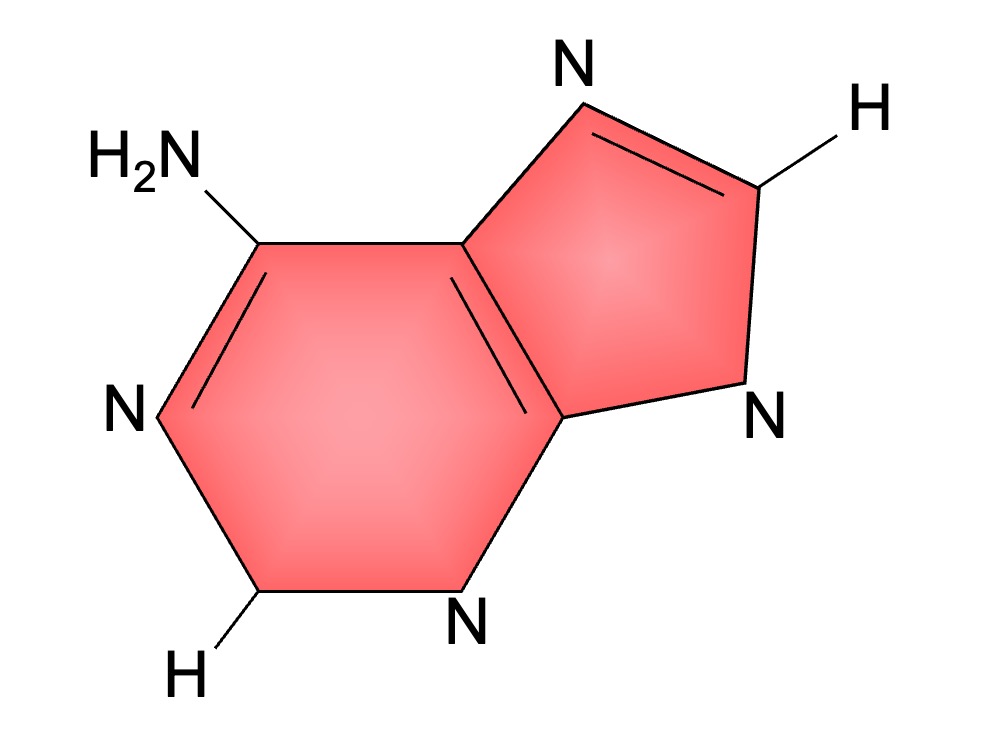
Adenine
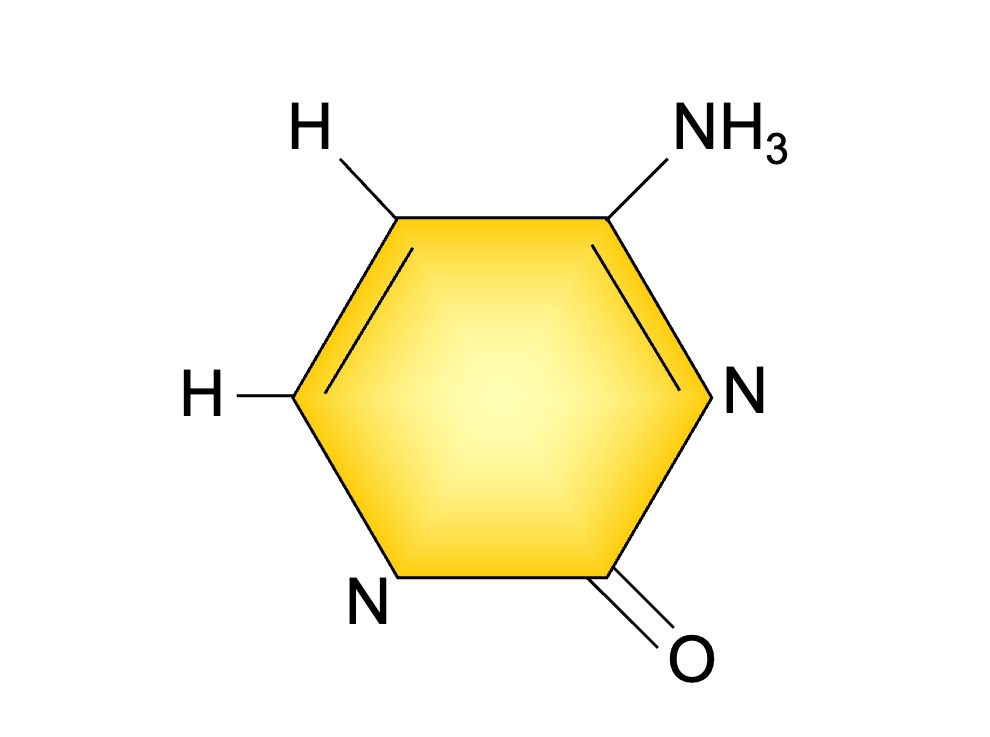
Cytosine
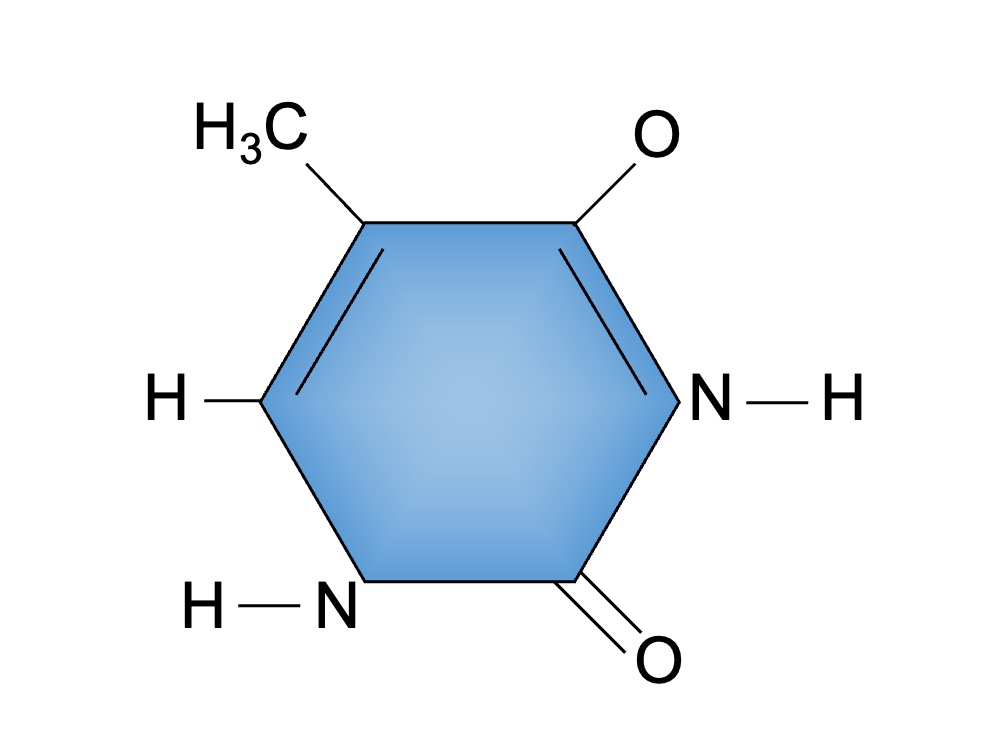
Thymine
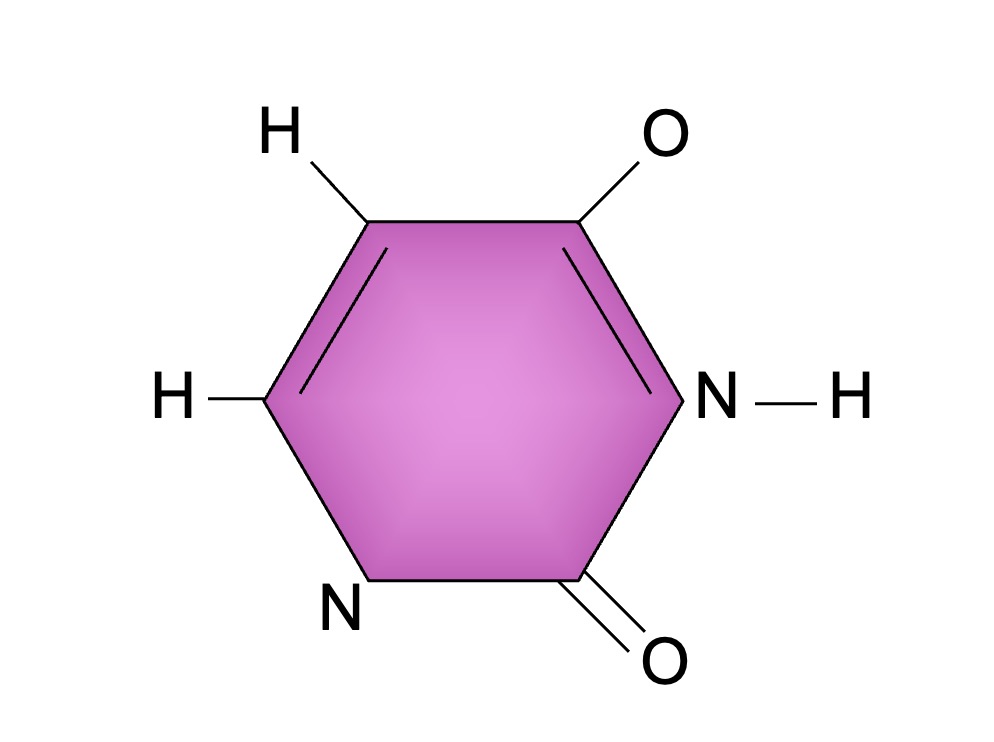
Uracil
The order of the bases in the nucleotide sequence forms the basis for the genetic instructions
-
Different instructions have different base sequences – just like how different combinations of letters make different words
The nitrogenous bases can pair up (purine : pyrimidine) via hydrogen bonding to create a complementary sequence
-
Guanine always pairs with cytosine, while adenine always pairs with thymine (DNA) or uracil (RNA)
The capacity for nucleic acids to undergo complementary base pairing is critical to its function as a genetic code
-
It allows for the genetic information to be replicated (one strand acts as a template for the synthesis of a new strand)
-
It allows for the genetic instructions to be expressed within the cell (a complementary transcript can be produced from the template)
Complementary Base Pairing

Thymine / Uracil pairs to Adenine