Autotrophs
Autotrophs synthesise organic molecules from simple inorganic substances obtained from the abiotic environment
-
These inorganic materials are obtained from the air (oxygen, carbon dioxide), soil (nitrates, phosphates) and water
Most autotrophs use photosynthesis as the mode of autotrophic nutrition, whereby light is used as an initial energy source
-
Examples of photosynthetic organisms include all plants, most types of algae and several groups of bacteria (cyanobacteria)
Photoautotrophs
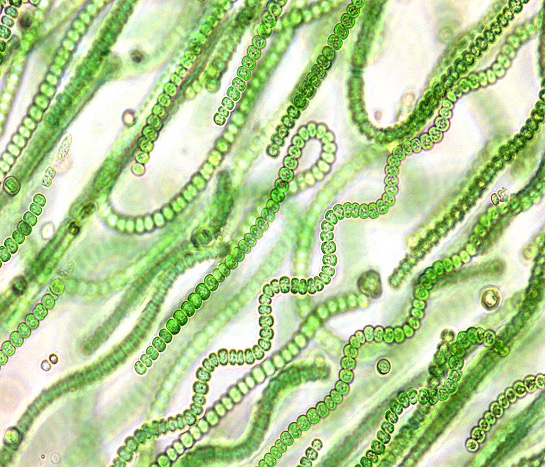
Cyanobacteria
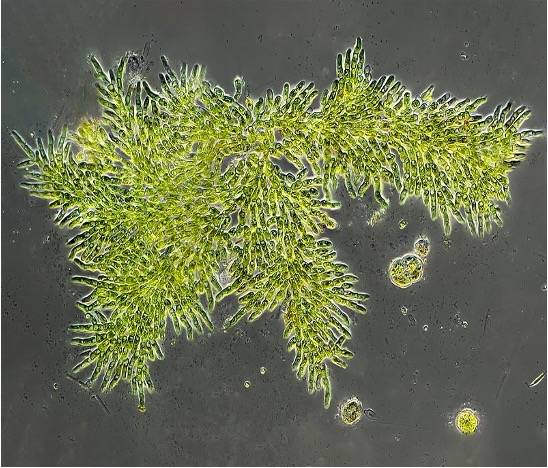
Algae

Plants
Plant Adaptations
Plants may possess a variety of adaptations to maximise their ability to absorb light for photosynthesis
-
Lianas: Woody vines that are rooted in the soil and use the trunks of trees to reach the canopy
-
Overstory: Emergent trees can grow above the canopy to gain the most sunlight for photosynthesis
-
Understory: Low-growing herbs and shrubs possess large leaves to maximise their surface area
-
Shade tolerant plants: Contain different photosynthetic pigments to absorb more wavelengths of light
-
Epiphytes: Plants that grow on the branches of other plants, with no direct contact with the soil
-
Strangler epiphytes may grow roots down to the soil to compete with a host plant for resources
-