Amino Acids
Proteins are composed of long chains of recurring monomers called amino acids
-
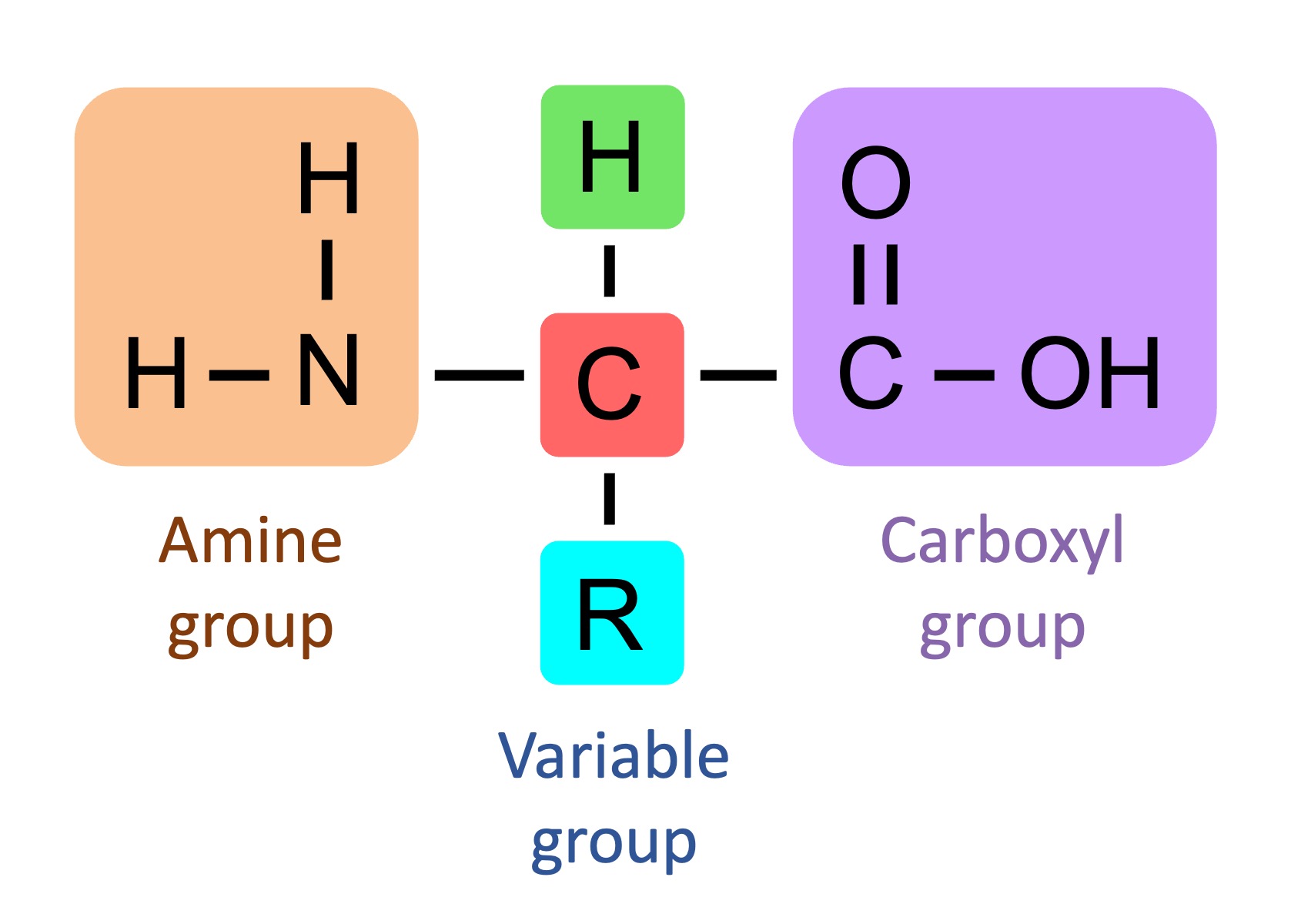
Each amino acid contains a central alpha carbon linked to an amine group, carboxyl group, a variable group and a hydrogen atom
There are 20 different amino acids which are universal to all living organisms
-
Each type of amino acid differs in the composition of their variable side chain (denoted ‘R’)
Amino Acid Structure
Amino acids can be either essential, non-essential or conditional according to dietary requirements
-
Essential amino acids cannot be produced by the body and must be present in the diet
-
Non-essential amino acids can be produced by the body (from other amino acids) and are therefore not required as part of the diet
-
Conditional amino acids can be produced by the body, but at rates lower than certain conditional requirements
-
In other words, they are essential at certain times only (such as during pregnancy, infancy or illness)
-
A shortage of one or more essential amino acids in the diet will prevent the production of specific proteins
-
This is known as protein deficiency malnutrition and the health effects will vary depending on the amino acid shortage
-
Certain diets (e.g. vegan) require particular attention to ensure essential amino acids are consumed and malnutrition is avoided