Types of Transport
Movement of materials across a biological membrane may occur either actively or passively and may involve different mechanisms depending on the permeability of the membrane to a particular material
Passive Transport
Passive transport involves the movement of material along a concentration gradient (high concentration ⇒ low concentration)
-
Because materials are moving down a concentration gradient, it does not require the expenditure of energy (ATP hydrolysis)
There are three main types of passive transport:
-
Simple diffusion – movement of small or lipophilic molecules that can freely cross the bilayer
-
Osmosis – movement of water molecules across the bilayer (dependent on solute concentrations)
-
Facilitated diffusion – movement of large or charged molecules via transmembrane proteins
Active Transport
Active transport involves the movement of materials against a concentration gradient (low concentration ⇒ high concentration)
-
Because materials are moving against the gradient, it does require the expenditure of energy (ATP hydrolysis)
There are two main types of active transport:
-
Primary active transport – A molecule is moved against its gradient using energy from the hydrolysis of ATP
-
Secondary active transport – A molecule is moved against its gradient coupled to another molecule moving down an electrochemical gradient (cotransport)
Types of Transport

Simple Diffusion
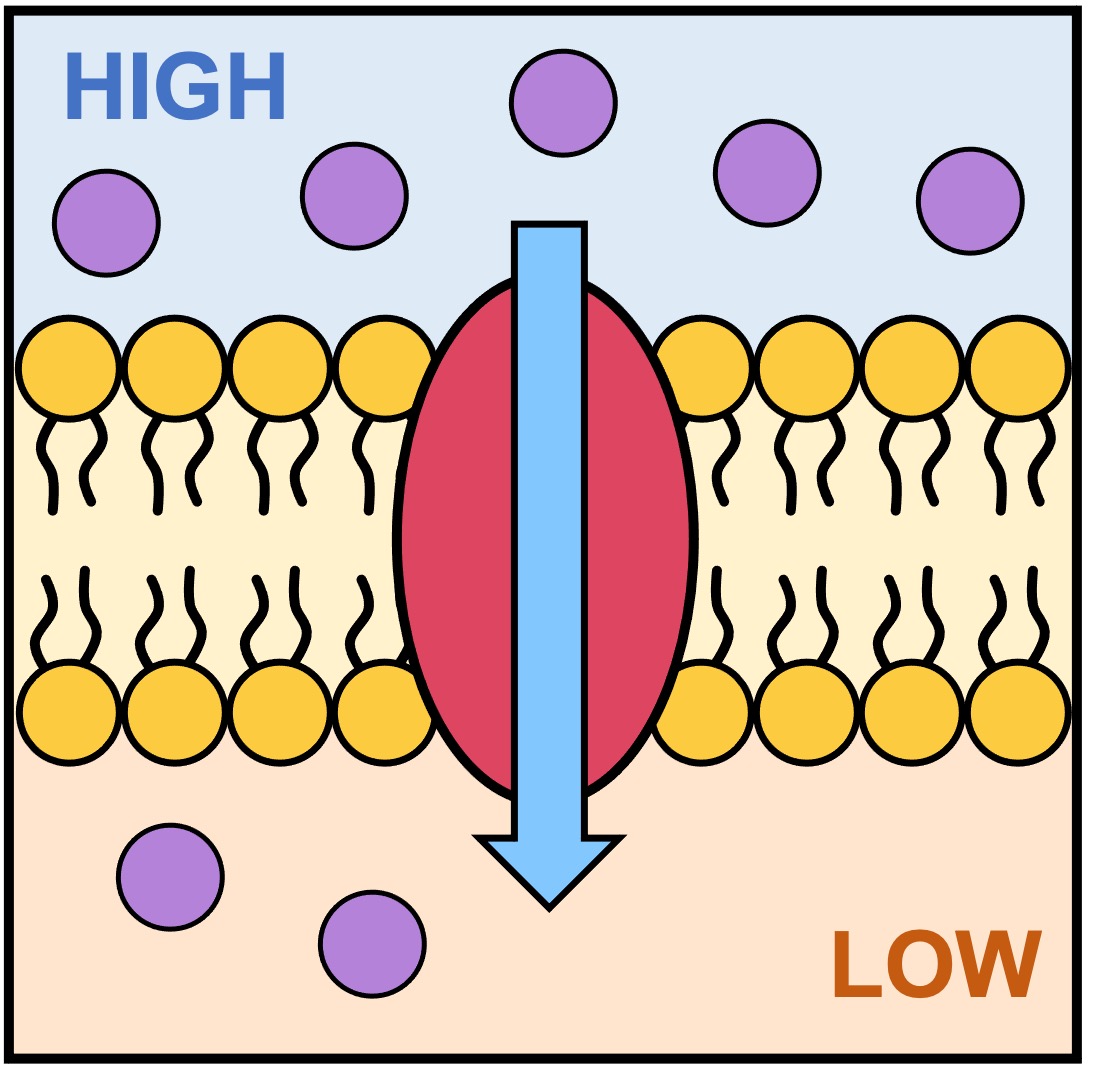
Facilitated Diffusion