Organic Compounds
An organic compound is a compound that contains carbon and is found in living things
-
Exceptions include carbides (CaC2), carbonates (CO32–), oxides of carbon (CO2) and cyanides (CN–)
Carbon forms the basis of all organic compounds due to its ability to form large and complex molecules via covalent bonding
-
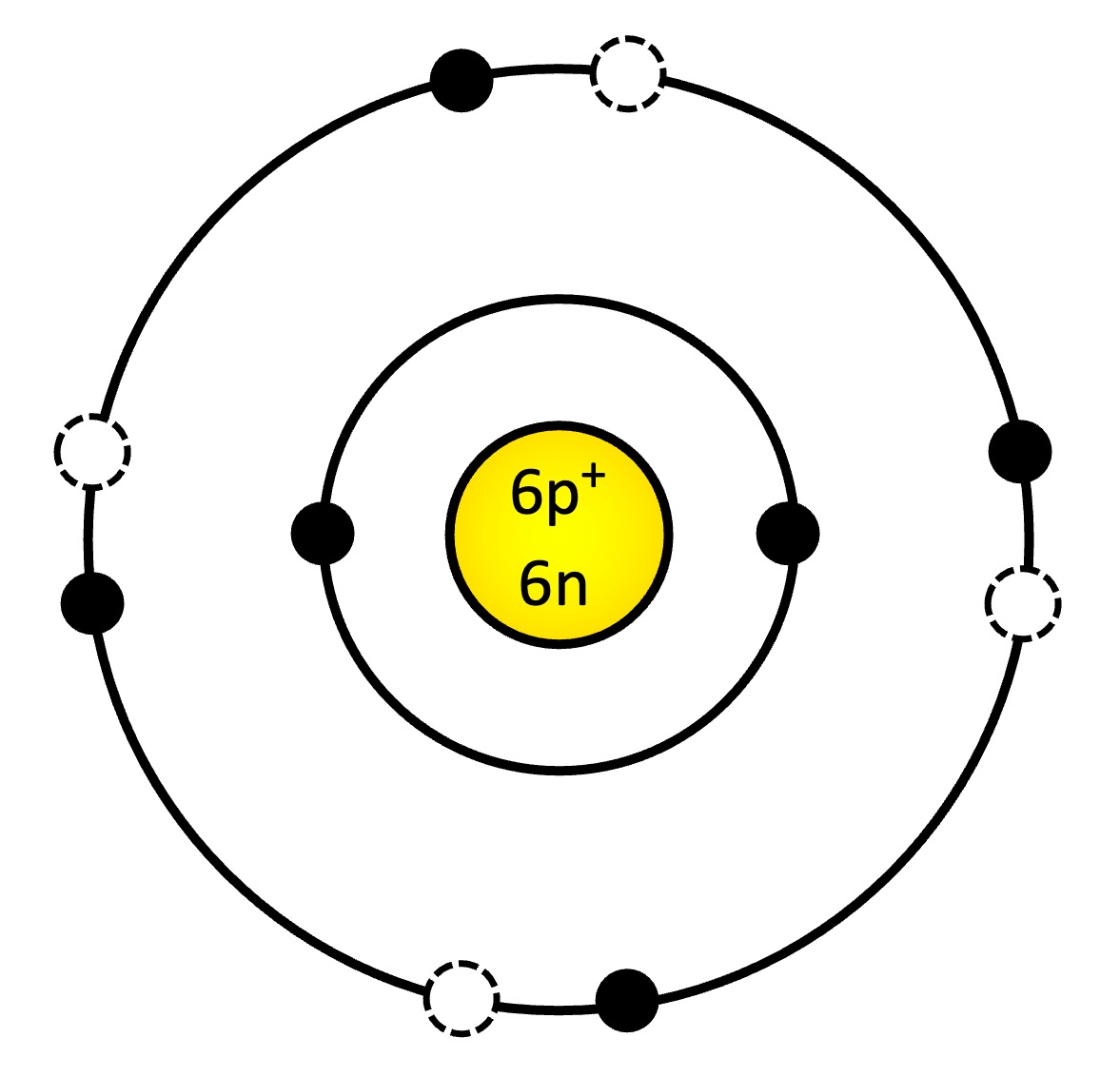
Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds, with bonds between carbon atoms being particularly stable
-
This allows carbon to form a wide variety of structures, including compounds consisting of branched or unbranched chains and single or multiple rings
Schematic of a Carbon Atom
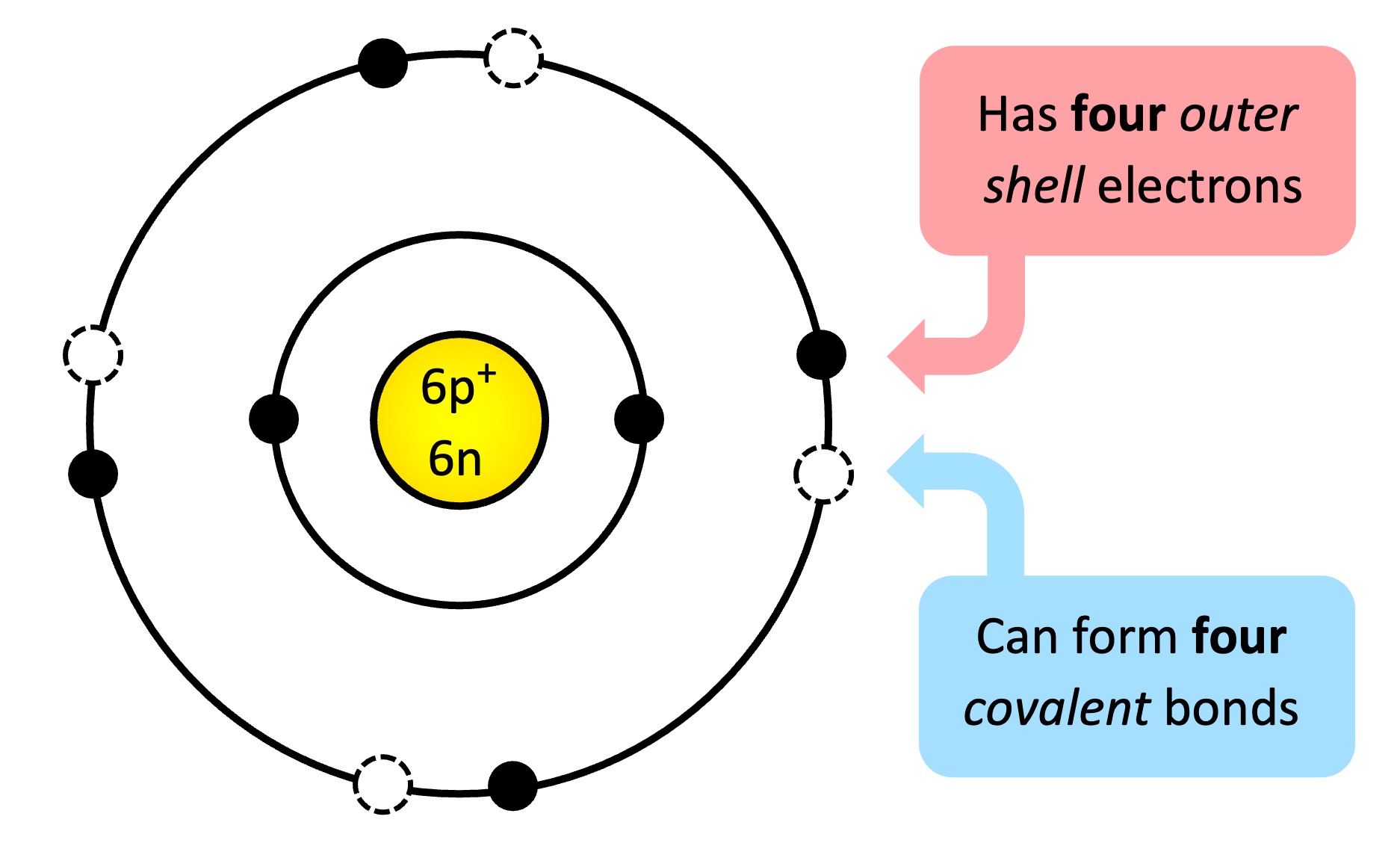
Carbon Atom
Types of Carbon Compounds
There are four main groups of organic compounds that contribute to the structure and function of a cell
Carbohydrates
-
Carbohydrates are molecules consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) – typically in a consistent ratio of (CH2O)n
-
The monomeric subunit of a carbohydrate will commonly adopt a closed ring structure that can form different stereoisomers
-
Carbohydrates are commonly used in nutrition as an energy source, but can also be used in cell recognition (glycoproteins) and structure (cellulose)
-
The monomeric subunits are also used as components in a range of different molecules, including DNA and coenzymes (ATP and NADH)
Lipids
-
Lipids are non-polar hydrophobic molecules that typically consist of either unbranched chains (fatty acids) or ringed structures (steroids)
-
Lipids serve as the main structural component of cell membranes (phospholipids and cholesterol) and may also be utilised for energy storage (triglycerides)
-
Certain lipids may also function as signalling molecules (steroid hormones)
Nucleic Acids
-
Nucleic acids consist of monomeric subunits (nucleotides) containing a pentose sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base
-
Nucleic acids function as the genetic material of the cell and determine the inherited features of an organism
-
There are two main types of nucleic acids – DNA functions as a master copy, while RNA is responsible for protein assembly
Proteins
-
Proteins are composed of one or more chains of amino acid residues and comprise over 50% of the dry weight of the cell
-
They perform a vast array of functions within the cell – including catalysis (enzymes), structure, signalling and transport
-
Some proteins can have non-peptide groups attached (cofactors / prosthetic groups) which contribute to the overall function of the molecule
Organic Compounds

Carbohydrate

Lipids

Nucleic Acid

Protein