Fertilisation
Fertilisation is the process whereby the haploid gametes (egg and sperm) fuse together to form a diploid zygote
-
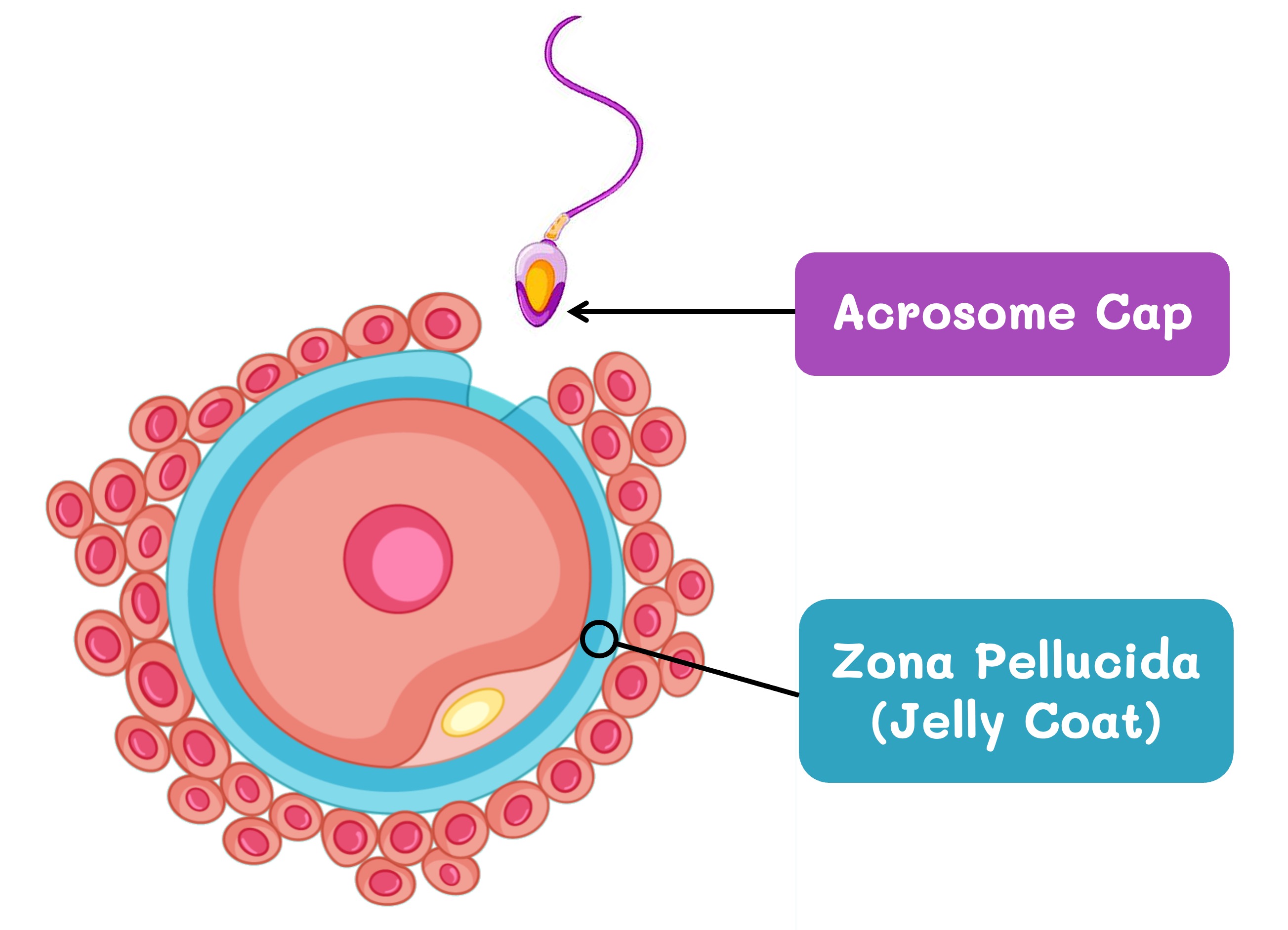
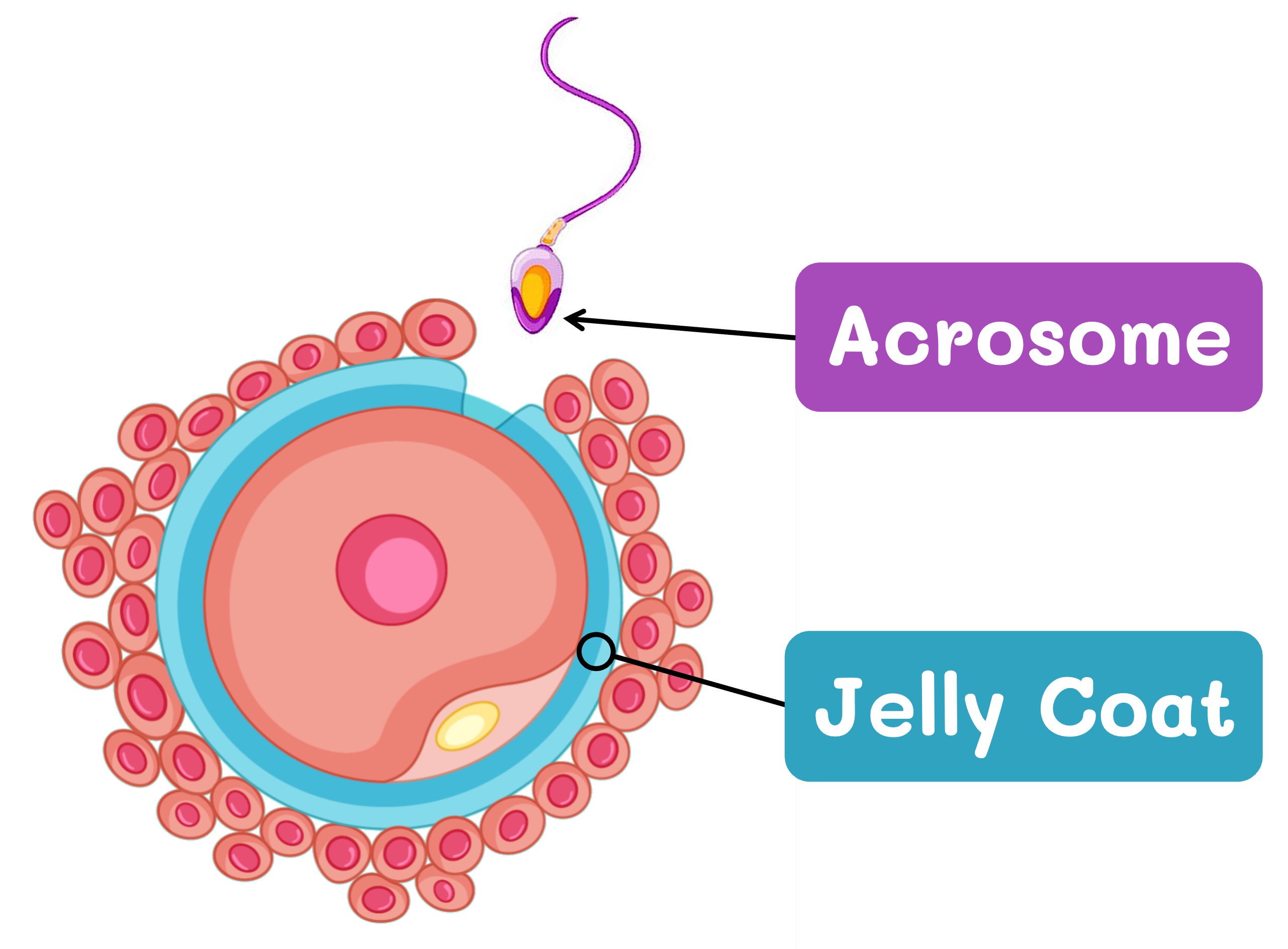
The egg cell is surrounded by an extracellular matrix called the zona pellucida (jelly coat) which protects against sperm penetration
-
Successful fertilisation involves two key processes – the acrosome reaction and the cortical reaction
Acrosome Reaction:
When the sperm reaches an egg, the acrosome reaction allows the sperm to break through the surrounding jelly coat
-
The sperm pushes through the follicular cells of the corona radiata and binds to the zona pellucida (jelly coat)
-
The acrosome vesicle fuses with the jelly coat and releases digestive enzymes which soften the glycoprotein matrix
-
The sperm then pushes its way through the softened jelly coat and binds to exposed docking proteins on the egg membrane
-
The membrane of the egg and sperm then fuse and the sperm nucleus (and centriole) enters the egg
Cortical Reaction:
The cortical reaction occurs once a sperm has successfully penetrated an egg in order to prevent polyspermy
-
Cortical granules within the egg’s cytoplasm release enzymes (via exocytosis) into the zona pellucida
-
These enzymes destroy sperm binding sites and also thicken and harden the glycoprotein matrix of the jelly coat
-
This prevents other sperm from being able to penetrate the egg (polyspermy), ensuring the zygote formed is diploid
Egg and Sperm