Energy Sources
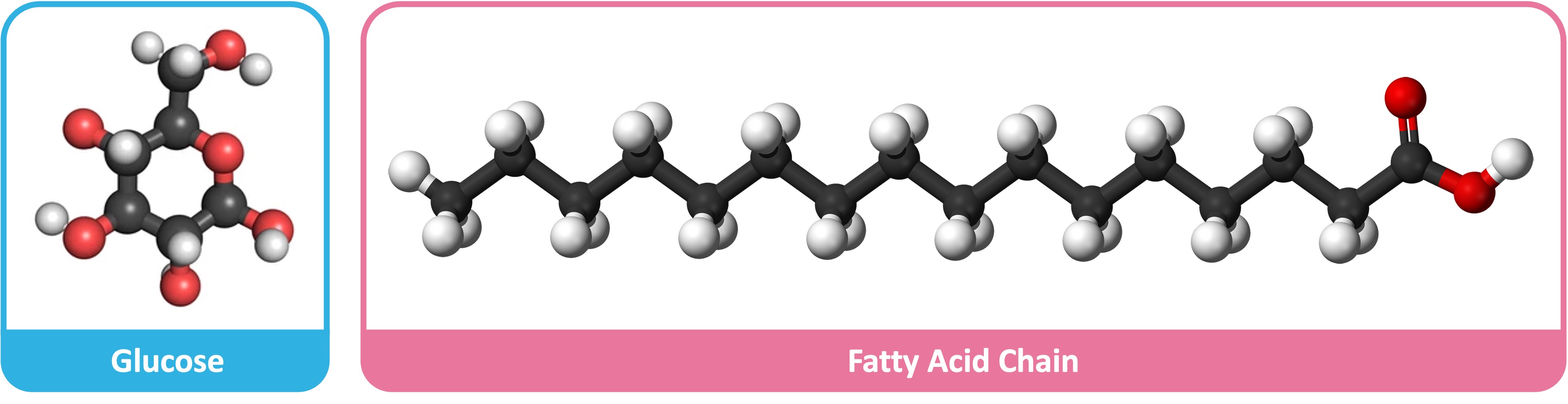
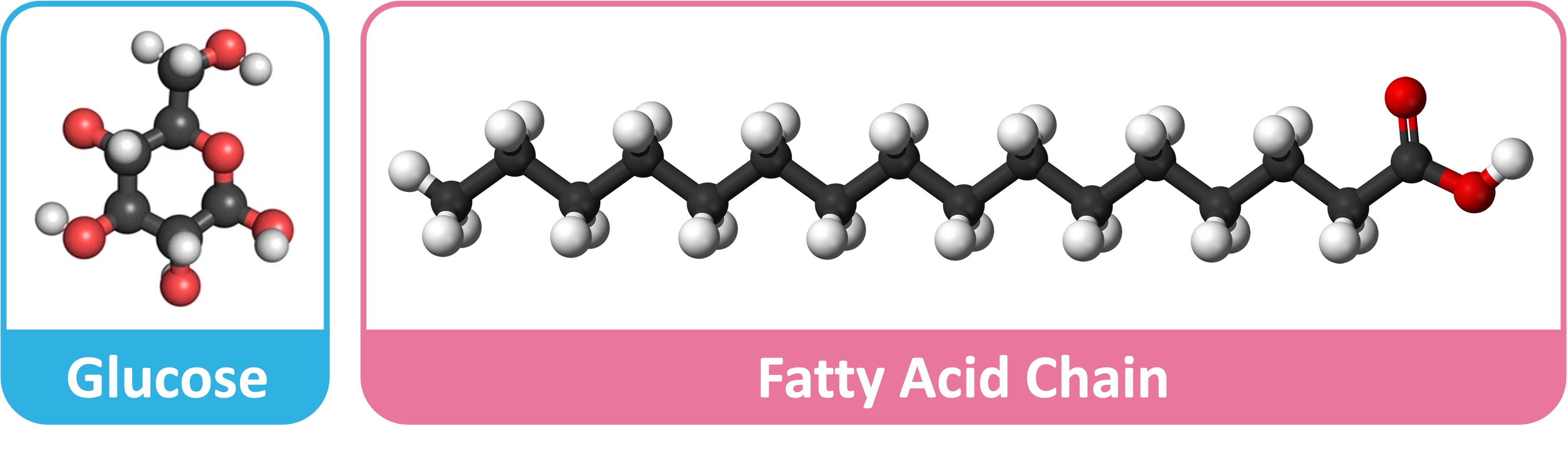
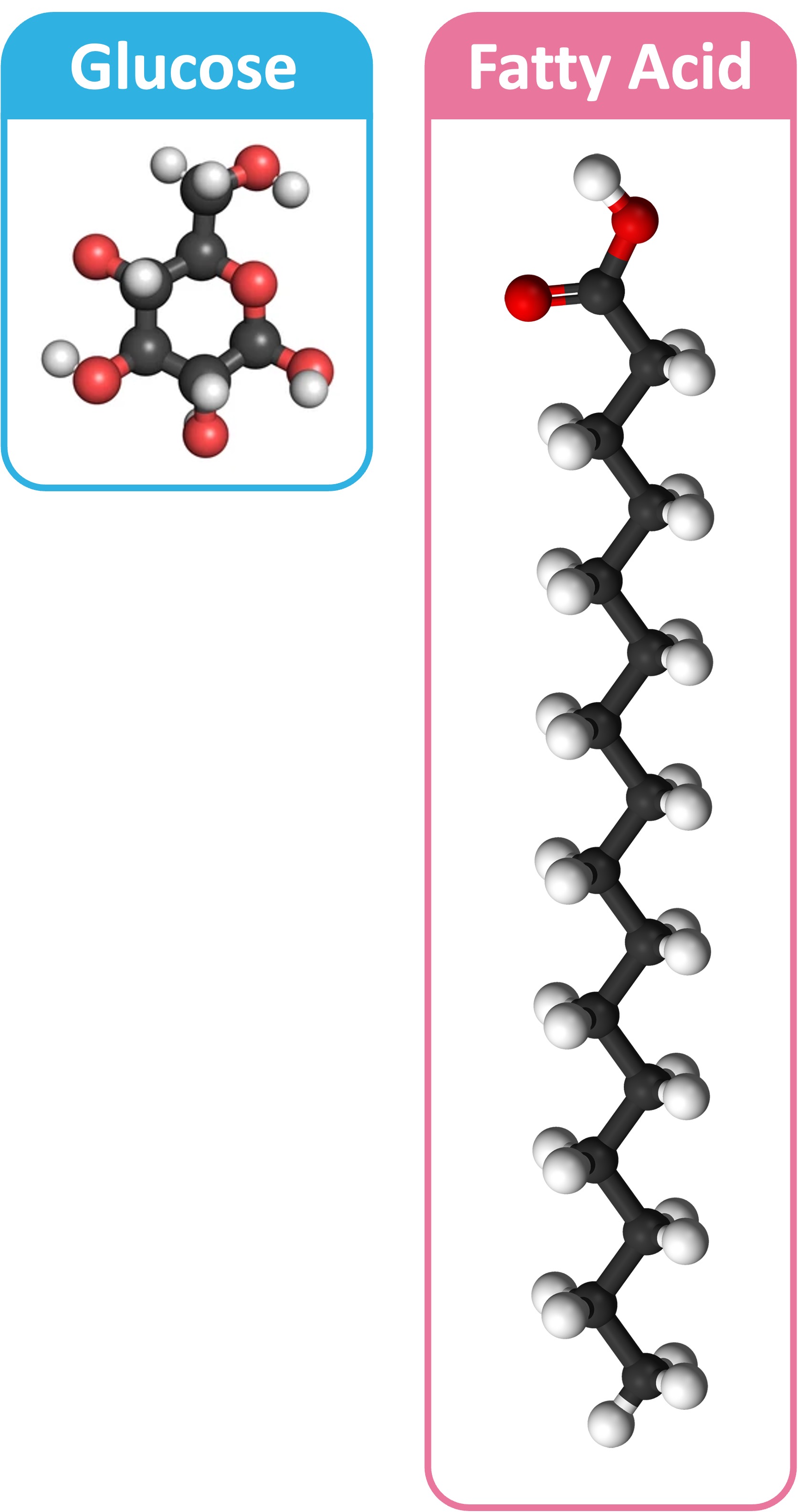
Carbohydrates are the most commonly used respiratory substrates because they are easier to digest and transport
-
Carbohydrates can be broken down into monosaccharides (e.g. glucose) which are able to be used in glycolysis
Lipids are used as a long-term source of energy as they are easier to store within the body (non-polar = less osmotic effect)
-
Fatty acid chains are broken down into 2C compounds (to form acetyl CoA), so they can only be digested aerobically (bypasses glycolysis)
-
Lipids also produce more energy per gram as the carbon chains possess less oxygen and have more oxidizable hydrogen and carbon
Carbohydrates vs Lipids